Trading Journal Example: Boost Your Trading Results Today
Unlock Your Trading Potential with the Right Journaling Method
Download my FREE TRADING JOURNAL HERE
A trading journal is key to consistent trading profits. This listicle provides six trading journal examples to help you find the perfect fit. Whether you prefer a spreadsheet, dedicated software, a notebook, visual aids, a focus on psychology, or platform integration, we’ve got you covered. Discover how the right trading journal example can improve your strategy, manage risk, and boost profitability in 2025. Learn from these examples and unlock your trading potential.
1. Spreadsheet Trading Journal
A spreadsheet trading journal is a powerful tool for tracking and analyzing your trading performance using spreadsheet applications like Microsoft Excel or Google Sheets. This is arguably the most popular method for maintaining a trading journal due to its flexibility, accessibility, and robust data analysis capabilities. By leveraging customizable tables, formulas, and charts, traders can systematically record every trade, understand their strengths and weaknesses, and ultimately improve their profitability. This trading journal example is highly effective for identifying patterns and improving trading strategies.
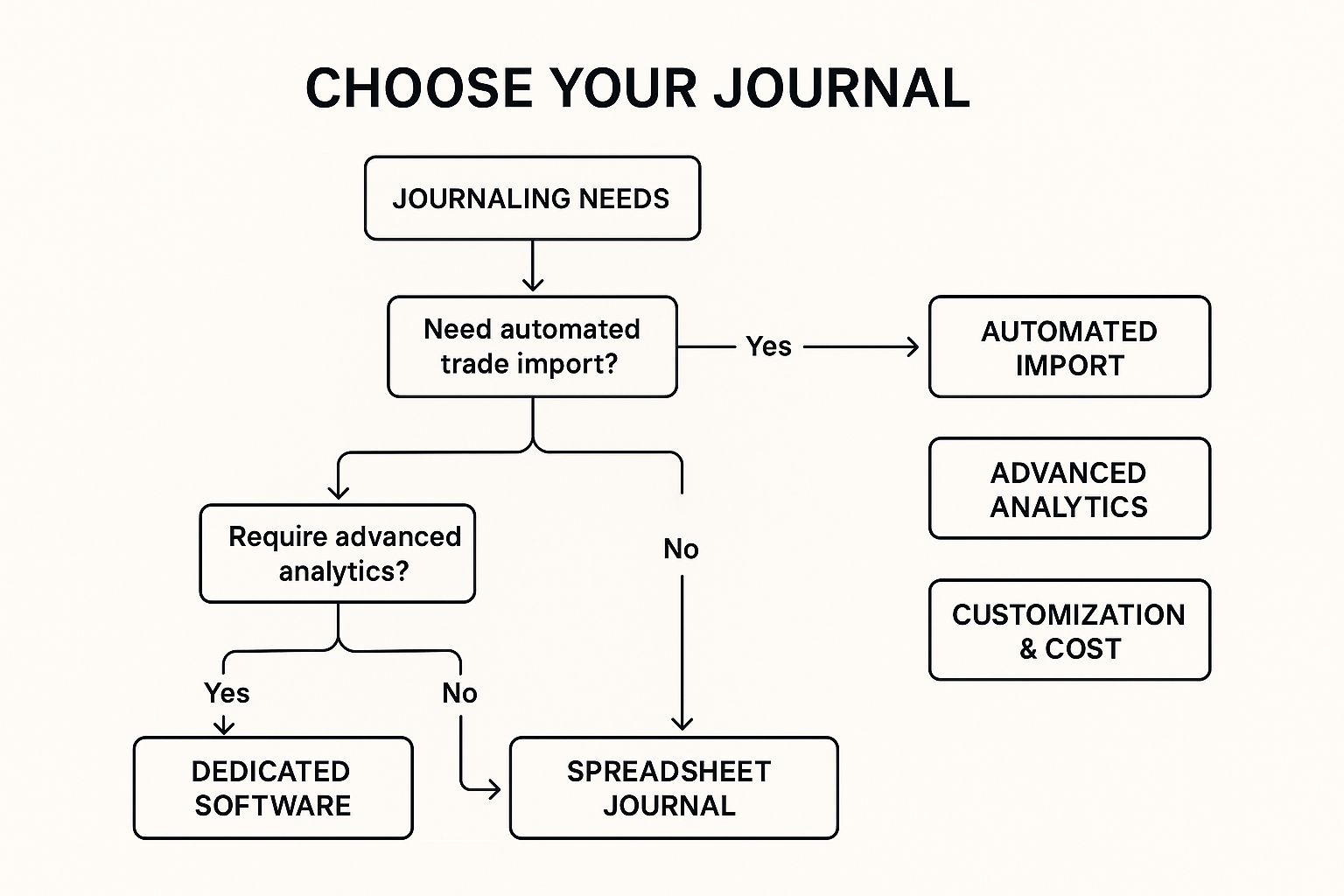
The infographic presents a decision tree to help traders determine if a spreadsheet trading journal is right for them. The primary decision point revolves around the trader’s comfort level with spreadsheets. If comfortable, the path leads towards leveraging the spreadsheet’s features like customization and analysis. If not, alternative journal methods are suggested. From there, the tree branches into considerations of cost and data analysis needs, guiding users to the most suitable approach for their specific situation. This decision flow helps traders quickly assess whether a spreadsheet-based journal aligns with their technical skills and trading requirements.
This method deserves its place on this list because it offers a practical and affordable solution for traders of all levels. Beginners can easily get started, while experienced traders can leverage its advanced features. Its versatility allows you to track anything from simple day trades to complex options strategies.
Features and Benefits:
- Customizable columns and layout: Tailor the journal to your specific needs and trading style.
- Automatic calculations: Automatically calculate profit/loss, win rate, and other key metrics.
- Data visualization: Create charts and graphs to visualize your trading performance over time.
- Filtering and sorting: Easily filter and sort trades by instrument, strategy, or any other criteria.
- Import/export functionality: Import data from your brokerage account or export it for further analysis.
- Statistical analysis tools: Utilize spreadsheet functions to perform statistical analysis on your trading data.
Pros:
- Low or no cost: Free with Google Sheets and readily available with Microsoft Excel.
- High degree of customization: Adapt the journal to any trading style or strategy.
- Powerful data analysis capabilities: Leverage spreadsheet functionalities for in-depth performance analysis.
- Accessible across multiple devices: Access your journal from your computer, tablet, or phone.
- Easy to backup and share: Easily create backups and share your journal with mentors or colleagues.
- No learning curve for those familiar with spreadsheets: If you know how to use spreadsheets, you can start immediately.
Cons:
- Manual data entry can be time-consuming: It requires manual input for each trade, which can be tedious.
- Limited integration with trading platforms: Direct data import from trading platforms may not be available.
- Can become unwieldy with large amounts of data: Large datasets can make the spreadsheet slow and difficult to manage.
- Limited visual representation of trades compared to specialized software: While charts are possible, visualization options might be less sophisticated than dedicated trading journal software.
- Requires regular maintenance and updating: Maintaining formulas and ensuring data accuracy requires ongoing effort.
Examples:
Tips for using a Spreadsheet Trading Journal:
- Include columns for date, instrument, position size, entry price, exit price, profit/loss, and especially trade rationale. The “why” behind your trades is crucial for learning.
- Use conditional formatting to highlight winning and losing trades for quick visual identification.
- Create separate tabs for different strategies or timeframes to keep your data organized.
- Schedule weekly and monthly review sessions to analyze your performance and identify areas for improvement.
- Use pivot tables to identify patterns in your trading and gain valuable insights.
- Include screenshots of trades in a separate column for a visual record of your entries and exits. This is particularly helpful for price action traders.
Popularized By:
- Mark Douglas (Trading in the Zone)
- Alexander Elder (Trading for a Living)
- TraderSync
When and why to use this approach: A spreadsheet trading journal is ideal for traders who are comfortable with spreadsheets and want a cost-effective, highly customizable solution. It’s suitable for all experience levels, from beginners to professionals. It’s particularly beneficial for traders who enjoy in-depth data analysis and want to uncover hidden patterns in their trading behavior. While manual data entry can be time-consuming, the insights gained often outweigh the effort.
2. Dedicated Trading Journal Software
For traders serious about improving their performance, dedicated trading journal software offers a powerful alternative to spreadsheets or handwritten notes. This type of software provides a purpose-built platform specifically designed for logging, analyzing, and reviewing your trades, offering a range of features that can significantly enhance your understanding of your trading activity. This makes it a valuable trading journal example for those seeking to take their analysis to the next level.

These platforms function as centralized hubs for all your trading data. They often allow automated import of trades directly from your brokerage account, eliminating manual entry and saving valuable time. Once imported, the software automatically calculates key performance metrics and statistics, providing deeper insights into your strengths and weaknesses. Advanced features like trade replay and visual trade representation on charts allow you to meticulously review your entries and exits, identifying patterns and areas for improvement. Risk analysis tools help you manage and optimize your position sizing and overall risk exposure. The ability to tag trades with specific strategies and market conditions allows for granular filtering and analysis, enabling you to isolate the most (and least) profitable aspects of your trading.
Examples of successful implementation:
- Tradervue: Popular among day traders, Tradervue offers social sharing features, allowing you to connect with other traders and share your performance (www.tradervue.com).
- TraderSync: Known for its robust trade replay and detailed analytics, TraderSync provides a deep dive into your trading behavior, helping you identify recurring mistakes and optimize your strategies. (www.tradersync.com)
- TradeMetria: Geared towards statistical analysis and performance metrics, TradeMetria empowers you to backtest strategies and optimize your approach based on hard data. (www.trademetria.com)
Pros:
- Saves time through automated trade import
- Provides deeper performance insights than spreadsheets
- Offers visual representation of entries and exits
- Specifically designed for trading workflow
- Regular updates with new features
- Professional-grade analytics
Cons:
- Monthly subscription costs
- Learning curve to utilize all features
- May not integrate with all brokers
- Less customizable than spreadsheets
- Potential privacy concerns with cloud-based services
Actionable Tips for Using Trading Journal Software:
- Free Trials: Take advantage of free trial periods offered by most platforms to find the best fit for your needs.
- Broker Compatibility: Ensure your broker is supported before committing to a subscription.
- Focus on Analysis: Don’t just log trades; actively use the analytical tools to identify patterns and improve your performance.
- Regular Reviews: Schedule regular review sessions using the software’s reporting features.
- Tagging: Tag trades with strategies and market conditions for more granular analysis.
- Trade Replay: Utilize the trade replay feature to identify mistakes and pinpoint areas for improvement.
When and Why to Use This Approach:
This type of trading journal example is ideal for traders who are committed to continuous improvement and want to move beyond basic trade logging. If you’re looking for a powerful tool to analyze your performance, identify weaknesses, and refine your trading strategies, dedicated trading journal software is an excellent investment. It is particularly beneficial for traders who execute a high volume of trades, as manual entry into spreadsheets quickly becomes cumbersome. This method is well-suited for all trader types, from novice to experienced, who are serious about achieving consistent profitability. Using software helps streamline your workflow and unlock valuable insights that might otherwise be missed.
3. Physical Trading Journal (Notebook)
A physical trading journal offers a tangible, handwritten approach to documenting your trading journey. This traditional method involves manually recording every trade, accompanying thought processes, market observations, and emotional responses using a simple notebook or a specialized trading journal. This creates a deeply personal and readily accessible narrative of your trading decisions and their outcomes, serving as a powerful tool for self-analysis and continuous improvement. This method provides a trading journal example that is both effective and time-tested.

The beauty of a physical journal lies in its complete customizability. You are free to design a format that perfectly suits your trading style and analytical needs. Unlike digital platforms, there are no software limitations or pre-set fields. This allows you to incorporate drawings, charts, and annotations directly within your entries, providing a holistic view of each trading scenario. Sections dedicated to pre-trade planning and post-trade analysis encourage a structured approach to decision-making and performance evaluation. Moreover, the tactile experience of writing by hand has been shown to enhance memory retention, solidifying lessons learned from both successes and failures.
Features:
- Completely customizable format
- No technology requirements
- Permanent physical record
- Space for drawings, charts, and annotations
- Sections for pre-trade planning and post-trade analysis
- Tactile experience that enhances memory retention
Pros:
- Enhances learning through physical writing
- No technical issues or crashes
- Promotes deeper reflection and mindfulness
- No subscription costs (one-time purchase)
- Privacy – no data stored in cloud services
- No distractions from notifications or other applications
Cons:
- Cannot automatically calculate statistics
- Limited space and organization options
- Difficult to search through historical entries
- Time-consuming to maintain
- No backup unless manually created
- No integration with trading platforms
Examples:
- The Trading Journal Notebook by Peter Brandt
- MTrading Journal (specialized trading notebook)
- Leuchtturm1917 hardcover journals (popular choice among professional traders)
Tips for Successful Implementation:
- Create a Consistent Template: Develop a standardized format for each page to ensure consistency and easy review. Include sections for entry/exit points, rationale, market conditions, emotional state, and outcome.
- Focus on Emotions: Dedicate a section to recording your emotional state before, during, and after each trade. This helps identify emotional biases that may be impacting your decisions.
- Use Visual Aids: Employ colored pens to highlight different types of trades or outcomes. Include small printouts of charts or screenshots to provide visual context.
- Schedule Dedicated Time: Set aside specific time each day or week for journal writing to maintain consistency and avoid neglecting this crucial practice.
- Develop an Index: Create an index page to catalog trades and lessons learned, making it easier to locate specific entries for future reference.
- Regular Review: Review your journal weekly and monthly to identify recurring patterns, successful strategies, and areas for improvement. Summarize key insights at regular intervals.
Why This Method Deserves Its Place in the List:
The physical trading journal provides a trading journal example that’s fundamental for developing trading discipline and self-awareness. While lacking the automation of digital platforms, it fosters a deeper connection with the trading process through the act of writing. This intentional engagement encourages mindful analysis and reinforces learning, ultimately contributing to improved decision-making and consistent performance. This method is particularly valuable for beginners seeking to establish solid trading habits, as well as experienced traders who value the benefits of introspection and a tactile learning experience. This method has been popularized by renowned figures like Peter Brandt (professional commodity trader), Mark Douglas (trading psychology author), and Jack Schwager (Market Wizards series). They all highlight the importance of meticulously documenting trades and reflecting on the psychological aspects of trading, and a physical journal facilitates exactly that.
4. Visual Trading Journal
The Visual Trading Journal is a powerful trading journal example that prioritizes visual learning and pattern recognition. Unlike traditional text-heavy journals, this method relies heavily on screenshots of charts with detailed annotations, creating a visual timeline of your trading development. This approach allows traders to quickly grasp recurring market structures and develop a stronger visual memory of their trades, making it easier to identify successful patterns and avoid repeating mistakes. This method is particularly effective for visual learners who benefit from seeing the evolution of a trade unfold on the chart itself.
This visual approach focuses on “before, during, and after” snapshots of trades. The “before” image showcases the setup and market context leading to the entry. The “during” image captures the trade’s progress and any adjustments made. The “after” image displays the exit point and the final outcome of the trade. Drawing tools are used to highlight key levels like support/resistance, trendlines, and specific chart patterns. Minimal text accompanies these visuals, focusing on crucial observations and decision-making rationale. This streamlined approach fosters quicker review and analysis.
Examples of Successful Implementation:
- OneNote or Evernote: These platforms allow for easy organization of tagged screenshots within notebooks, making retrieval and review efficient.
- TradingView Saved Charts: The built-in annotation tools within TradingView make it a seamless platform for creating and storing visual trading journals.
- PDF Compilations: Traders like Al Brooks exemplify the power of PDF compilations of annotated charts, showcasing specific trade setups and their outcomes.
Actionable Tips:
- Consistency is Key: Use consistent annotation symbols and colors to easily identify patterns.
- The Three Stages: Create “before, during, and after” sequences for each trade to capture the entire trade lifecycle.
- Multiple Timeframes: Include multiple timeframes for each setup to provide a broader market context.
- Concise Notes: Add brief text notes highlighting key observations and decision points.
- Organized Review: Organize your journal by pattern type or strategy for easier review and analysis.
- Weekly Review: Conduct weekly reviews to identify recurring successful and unsuccessful patterns.
- Dynamic Replays (Advanced): Consider using screen recording software for a dynamic replay of market conditions during the trade.
When and Why to Use This Approach:
The Visual Trading Journal deserves its place in this list because it offers a uniquely intuitive and effective way to learn from trading experiences. This method is particularly valuable for:
- Novice traders seeking to learn foundational price action techniques.
- Intermediate traders frustrated with inconsistent strategies and looking for visual confirmation of their setups.
- Experienced traders aiming to refine their technical analysis skills and identify subtle patterns.
- Professionals desiring a flexible, location-independent way to document and review their trades.
- Self-paced learners looking for a proven, action-based method to improve their trading performance.
Pros:
- Makes pattern recognition more intuitive.
- Easier to identify recurring market structures.
- Creates a strong visual memory of trades.
- Particularly effective for visual learners.
- Helps identify chart patterns that lead to success or failure.
- Enhances technical analysis skills.
Cons:
- Storage space requirements for images can be significant.
- Can be time-consuming to capture and annotate properly.
- Less emphasis on quantitative analysis.
- Difficult to generate statistics from visual data.
- Requires additional tools for numeric tracking.
5. Psychological Trading Journal
A Psychological Trading Journal is a unique type of trading journal example that focuses primarily on the mental and emotional aspects of trading, rather than just the technical analysis or performance metrics. This approach recognizes that trading psychology is often the most challenging aspect of successful trading and aims to help traders develop emotional intelligence and discipline. Instead of solely logging entry and exit points, a psychological trading journal delves into your mental state before, during, and after each trade. This allows you to identify patterns in your thinking and emotional reactions that might be sabotaging your results, even if your technical analysis is sound.
How it Works:
The core of this journaling method involves honestly recording your emotions, thoughts, and cognitive biases that influence your trading decisions. You’ll document your feelings before entering a trade (e.g., fear, greed, excitement), your emotional responses during the trade (e.g., anxiety, impatience, doubt), and your reactions after the trade concludes (e.g., regret, euphoria, frustration). By meticulously tracking these elements, you can start to see connections between your emotional state and your trading performance.
Examples of Successful Implementation:
Several successful traders and trading psychologists have championed this journaling method. Brett Steenbarger, a renowned trading psychologist, emphasizes the importance of daily psychological journaling to understand emotional influences on trading. Jared Tendler, a mental game coach, applies similar principles in his “Mental Game of Trading” journal approach. Rande Howell advocates for a “Mindful Trader” journal methodology incorporating mindfulness practices. These examples highlight the effectiveness of psychological journaling across various trading styles.
Actionable Tips for Your Trading Journal:
- Rate your emotional state: Use a 1-10 scale to rate your emotional state before and after each trade. This provides quantifiable data to track progress.
- Identify emotional triggers: Pinpoint specific events or market conditions that trigger strong emotional reactions and how these impact your decisions.
- Record physical sensations: Pay attention to physical sensations associated with trading emotions (e.g., racing heart, sweaty palms, tense muscles). This can provide valuable insights into your emotional state.
- Create a checklist: Develop a personal checklist of psychological best practices to review before each trading session.
- Link emotions to outcomes: Connect specific emotional states to trade outcomes to see patterns of behavior.
- Schedule weekly reviews: Dedicate time each week to review your journal and identify recurring psychological patterns.
- Consider a trading coach: Working with a trading coach can provide valuable guidance in interpreting your journal and developing personalized strategies for psychological improvement.
When and Why to Use a Psychological Trading Journal:
This approach is particularly beneficial for traders struggling with discipline and emotional control. It’s also valuable for those who find themselves deviating from their trading plan despite sound technical analysis. Essentially, if you suspect your psychology is impacting your trading performance, this type of journal can be invaluable.
Pros and Cons:
Pros:
- Addresses the often-overlooked psychological aspect of trading.
- Helps identify emotional triggers that lead to poor decisions.
- Builds self-awareness and emotional discipline.
- Creates accountability for psychological improvement.
- Complements technical analysis by explaining deviations from strategy.
Cons:
- Less focus on technical aspects and performance metrics.
- Requires honesty and vulnerability for effectiveness.
- Can be time-consuming due to the deep reflection required.
- Subjective nature makes standardization difficult.
- May be uncomfortable for traders who avoid emotional awareness.
This psychological trading journal example deserves its place in this list because it tackles the root cause of many trading struggles: our own minds. By understanding and managing our emotional responses to market fluctuations, we can make more rational decisions and improve our overall trading performance. While other trading journals might track entries, exits, and market conditions, the psychological trading journal focuses on the “inner game” of trading, a crucial element for long-term success. This method is relevant for traders of all levels, from novice to expert, as mastering trading psychology is a continuous process.
6. Trading Platform Integrated Journal
This approach to maintaining a trading journal example leverages the built-in features of your trading platform. It offers a streamlined method for documenting trades directly within the software you use for execution, creating a seamless workflow between action and reflection. This type of integrated journaling eliminates the need for separate spreadsheets or notebooks, keeping all your trading data in one central location.
Instead of switching between your trading platform and a separate journaling tool, you utilize features like chart annotations, notes tied to specific price levels and times, and built-in performance metrics. This allows for immediate documentation while the market context and your rationale are still fresh in your mind. Imagine marking your entry and exit points directly on the chart as you execute the trade, along with a brief note explaining your decision. Later, you can review these annotated charts to identify patterns in your trading and areas for improvement.
Features and Benefits:
- Direct annotation on charts: Visually connect your thoughts and analysis to price action.
- Integrated with execution data: Precisely record entry/exit points, trade size, and other key metrics automatically.
- Real-time journaling: Document your trades as they happen, capturing the immediacy of the market.
- Built-in performance metrics: Access platform-provided statistics to track your progress.
- Streamlined Workflow: No more switching between applications.
Examples of Successful Implementation:
- TradingView: Use drawing tools, text notes, and chart saving features to document your trades. TradingView’s social sharing capabilities also allow you to learn from other traders’ annotated charts, providing a rich source of trading journal examples.
- NinjaTrader: Leverage the Market Analyzer and journal functions to record trades and analyze performance.
- MetaTrader: Utilize the built-in journal features to document your trades directly within the platform.
- ThinkOrSwim: Use drawing tools and notes features to mark key levels and document trade rationale.
Pros:
- Streamlined workflow with no platform switching.
- Accurate recording of exact entry and exit points.
- Immediate documentation while information is fresh.
- Perfect synchronization between journal and actual trades.
- Reduced friction in the journaling process.
- Contextual notes with precise market conditions.
Cons:
- Limited by the capabilities of the trading platform.
- Features vary widely between platforms.
- Risk of data loss during platform updates.
- Often lacks comprehensive analytical tools for deeper dives into performance.
- May not allow for deeper reflection on emotional or psychological factors influencing trades.
- Tied to continued use of that specific platform.
Actionable Tips:
- Standardized Format: Develop a consistent structure for your notes to ensure clarity and easy review. For this trading journal example, consider noting the date, time, asset, entry price, exit price, position size, and a brief rationale for the trade.
- Screenshots: Take screenshots of key setups and annotated charts as a backup outside the platform.
- Color-Coding: Use different colors for different types of annotations (e.g., entries, exits, stop-losses).
- Regular Review: Schedule regular review sessions using the platform’s replay features to analyze past trades in context.
- Data Export: Regularly export your trading data to prevent potential loss during platform updates.
- Templates: Create templates with common annotations to save time and maintain consistency.
- Supplement for Psychology: Consider combining this method with an external journal for tracking emotional and psychological aspects of your trading.
When to Use This Approach:
This method is ideal for traders who value efficiency and prefer a streamlined workflow. It’s particularly well-suited for those who primarily focus on technical analysis and want to directly link their trades to chart patterns and indicators. Whether you’re a novice trader learning the ropes or an experienced professional, integrating your journal directly within your platform can significantly improve your trading process. However, remember to address the potential limitations by supplementing with external tools or methods as needed, especially for tracking the psychological aspects of trading.
Comparison of 6 Trading Journal Types
| Journal Type | 🔄 Implementation Complexity | ⚡ Resource Requirements | 📊 Expected Outcomes | 💡 Ideal Use Cases | ⭐ Key Advantages |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Spreadsheet Trading Journal | Moderate – requires spreadsheet skills and maintenance | Low – uses free or existing spreadsheet tools | Detailed quantitative analysis; customizable reports | Traders needing flexible, low-cost journaling with data control | High customization, powerful data analysis, cost-effective |
| Dedicated Trading Journal Software | High – software setup and learning curve | Medium to High – subscription fees and compatible devices | Automated tracking, advanced analytics, trade replay | Active traders wanting automation and deep insights | Automated import, professional analytics, visual trade tracking |
| Physical Trading Journal (Notebook) | Low – simple pen-and-paper method | Low – cost of notebook and writing materials | Introspective insights, tactile memory retention | Traders valuing mindfulness and privacy without tech dependence | Enhances reflection, no tech issues, privacy |
| Visual Trading Journal | Moderate – requires image capturing and annotation tools | Medium – storage for images and annotation software | Strong pattern recognition, intuitive visual records | Visual learners focusing on chart patterns and setups | Improves pattern recognition, visual memory enhancement |
| Psychological Trading Journal | Moderate – needs consistent emotional tracking | Low to Medium – journal or app for notes and assessments | Emotional awareness, discipline building, psychological insights | Traders struggling with discipline or emotional control | Builds self-awareness, identifies emotional triggers |
| Trading Platform Integrated Journal | Low to Moderate – depends on platform features | Low – uses existing trading platform tools | Streamlined journaling synchronized with trades | Day traders/scalpers needing seamless integration | Immediate documentation, exact trade data, no platform switching |
Elevate Your Trading with Consistent Journaling
A trading journal, regardless of its format – be it a spreadsheet, dedicated software, a physical notebook, a visual representation, a psychologically focused journal, or one integrated within your trading platform – acts as a mirror reflecting your trading performance. This article has explored various trading journal examples, each offering unique advantages. The key takeaway is that the most effective journal is the one you consistently use. By regularly reviewing your entries, you can identify recurring patterns in your wins and losses, pinpoint areas for improvement, and ultimately refine your strategies based on objective data rather than emotional impulses. Mastering these concepts is crucial for transforming from an inconsistent trader to a consistently profitable one. This translates to more informed decisions, better risk management, and a clearer path towards achieving your financial goals, whether that’s building a flexible, location-independent income or simply refining existing skills.
Developing a consistent writing process is crucial for improving your trading journal, enabling you to capture key details and insights effectively. Explore these different writing process examples to find a system that works for you. Source: Writing Process Examples: Boost Your Skills Today from Shy Editor.
Remember, the goal isn’t to achieve a perfect trading record, but to strive for continuous improvement. Find the trading journal example that resonates with you, adapt it to your individual needs, and watch it become your compass, guiding you toward trading mastery. Ready to take your trading to the next level and integrate powerful price action strategies into your analysis?
Ready to improve your trading with a proven, price action-focused approach? You can gain instant access to our world-renowned price action trading course.