Risk Management for Traders: Protect Your Investments Effectively
Why Risk Management Makes or Breaks Trading Careers
The exciting world of trading, with its promise of fast profits, often draws in individuals dreaming of overnight riches. Experienced traders, however, know a crucial truth: even the most brilliant trading strategies are worthless without robust risk management. This isn’t about dodging every loss. It’s about weathering the unavoidable downturns so you can seize future opportunities. Capital preservation is the top priority for professional traders. This may seem counterintuitive, but this approach to risk management builds a solid base for long-term success.
The Psychology of Risk
This focus on preservation isn’t just financial; it has a profound psychological impact. Clear risk parameters offer significant psychological advantages. For instance, defined risk levels reduce decision fatigue by pre-setting acceptable losses. Knowing your maximum risk also allows you to confidently execute trades when opportunities appear, without being held back by fear. This means traders can concentrate on spotting and using opportunities instead of being frozen by fear.
Measuring and Managing Risk
Traders manage risk by calculating key metrics. The infographic below illustrates three of these: average risk-reward ratio, average win rate, and maximum drawdown.
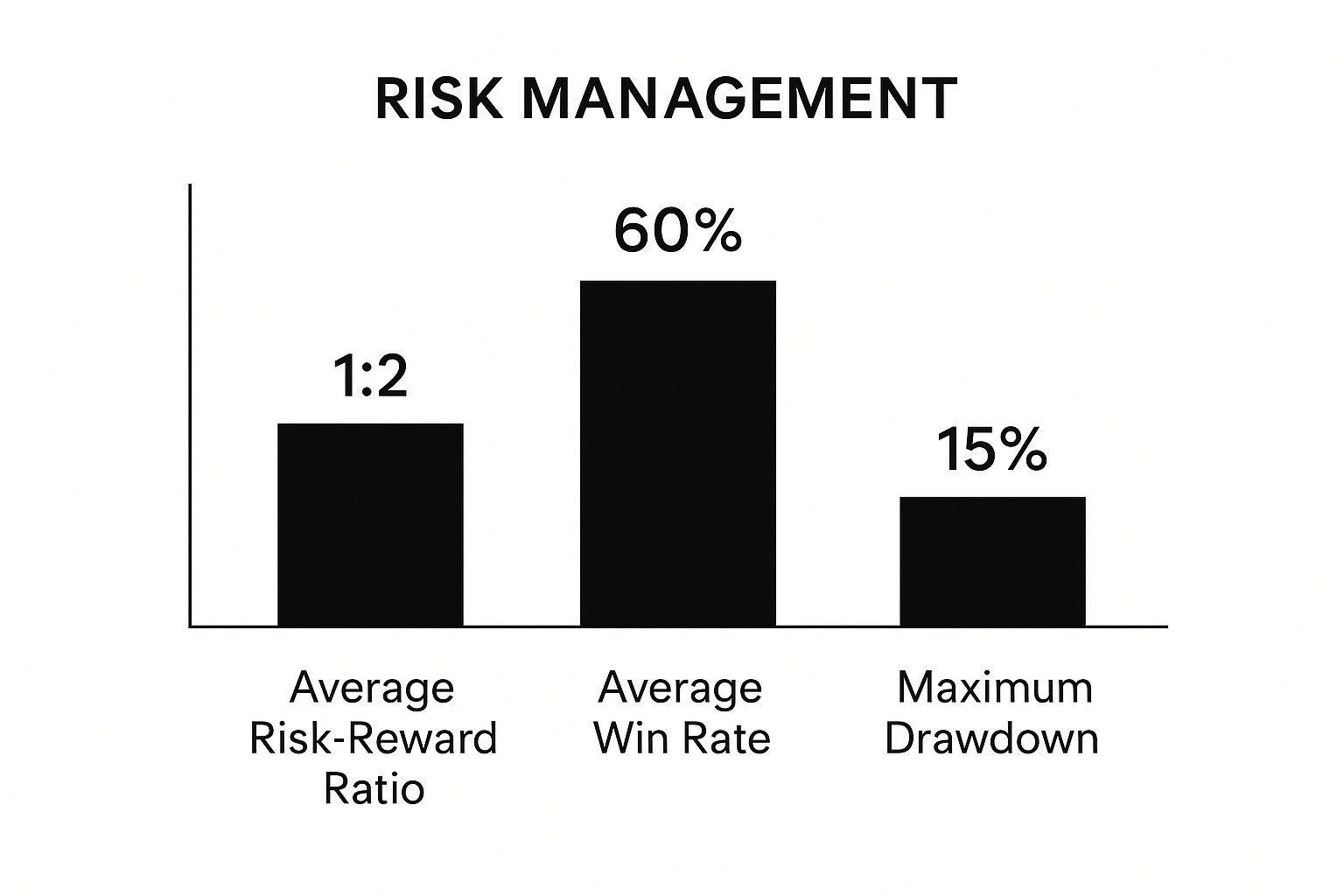
These metrics show a balanced approach. The win rate isn’t incredibly high, but the positive risk-reward ratio ensures profitability over time, with an acceptable maximum drawdown. This underscores how these metrics are interconnected and how they contribute to a sustainable trading strategy. A key advancement in risk measurement is Value-at-Risk (VaR). VaR calculates the potential loss in a portfolio over a set time and confidence level. This tool helps traders quantify their risk exposure for improved management. Learn more about VaR here: Explore this topic further.
To further illustrate the metrics used in risk management, let’s examine a table summarizing common ones:
The following table provides a brief overview of widely used risk metrics in trading. It compares their applications, strengths, and limitations.
Common Risk Management Metrics
| Risk Metric | Definition | Best Application | Limitations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Value-at-Risk (VaR) | Measures the potential loss in value of a portfolio over a specified period with a given confidence level. | Assessing portfolio risk and setting risk limits. | Doesn’t capture worst-case scenarios beyond the confidence level. |
| Maximum Drawdown | The peak-to-trough decline during a specific period. | Evaluating the largest historical loss and stress-testing strategies. | Past performance is not indicative of future results. |
| Risk-Reward Ratio | Compares the potential profit of a trade to the potential loss. | Determining the potential payoff relative to the risk taken. | Doesn’t guarantee consistent outcomes. |
| Win Rate | The percentage of winning trades. | Assessing the consistency of profitability. | Can be misleading without considering the size of wins and losses. |
| Sharpe Ratio | Measures risk-adjusted return, considering the volatility of an investment. | Comparing the performance of different investments or strategies. | Can be sensitive to the choice of risk-free rate. |
This table highlights the diverse tools available to traders for managing risk. Each metric offers a different perspective, and using them in combination can provide a more comprehensive understanding of risk exposure.
Case Studies: Risk in Action
Trading history offers numerous examples of traders with impressive early success who ultimately failed because of poor risk management. On the other hand, many traders have successfully weathered market crashes by sticking to strict risk protocols. These real-world stories show that consistently applying risk management principles is vital for long-term survival and profitability. This doesn’t mean eliminating all risk, but rather understanding and managing it within acceptable boundaries.
Position Sizing: The Most Underrated Trading Skill
Many traders fixate on finding the perfect entry point, believing it’s the key to profitability. But a critical element often neglected is position sizing: deciding how much capital to risk on each trade. This, in fact, is the true determinant of trading success. This section explores the art of position sizing, from its theoretical underpinnings to practical use in real-world trading.
Fixed-Percentage Risk Models
One common approach to position sizing is the fixed-percentage risk model. This strategy involves risking a fixed percentage of your trading capital on every trade, irrespective of your confidence level. For example, risking 1% of a $10,000 account means your maximum loss per trade is $100. This disciplined approach protects your account from being decimated by a few bad trades.
It also ensures that position size grows alongside your account, automatically scaling your trading as your capital increases. This offers traders steady risk management while using profits for growth. You might be interested in: How to master position sizing.
Volatility-Adjusted Position Sizing
While the fixed-percentage model is a good starting point, it doesn’t consider market volatility. Volatility-adjusted position sizing tackles this by incorporating a measure of price fluctuation. For a highly volatile stock, you might decrease your position size to maintain the same dollar risk.
Conversely, for a less volatile asset, you could increase position size while remaining within your risk tolerance. This dynamic adjustment ensures consistent risk exposure across varying market conditions.
The Kelly Criterion
A more complex approach is the Kelly Criterion, a mathematical formula for determining the optimal position size based on win rate and risk-reward ratio. Though powerful, it demands precise estimates of these parameters, which can be difficult in practice. However, grasping its core principles can offer valuable insights into balancing risk and reward.
Professional Position Sizing
Professional trading desks use complex position sizing models considering factors beyond volatility and risk-reward ratios. These may include market liquidity, asset correlation, and even tail risk scenarios. Understanding how professionals adapt their position sizing across different market conditions and asset classes can be invaluable for individual traders. This is particularly relevant in today’s active financial markets.
In recent years, the risk management market has expanded significantly, driven by market intricacy and the need for advanced risk management tools. It’s expected to increase from $12.09 billion in 2024 to $13.78 billion in 2025. Learn more about market growth statistics here: Find more detailed statistics here.

Common Position Sizing Mistakes
Many traders unknowingly harm their performance through small position sizing errors. Oversizing positions due to greed or overconfidence can lead to rapid account depletion. Undersizing, caused by fear or excessive caution, limits profit potential.
Even slight adjustments to position sizing can greatly affect risk-adjusted returns without changing the underlying trading strategy. This underscores the need to regularly review and refine position sizing practices.
Stop-Loss Mastery: Beyond Basic Price Levels

While position sizing helps determine how much to risk, stop-loss orders are essential for limiting potential losses on each trade. Simply setting a stop-loss based on a fixed price, however, often isn’t enough. This section explores advanced stop-loss techniques that move beyond basic price levels, emphasizing dynamic adjustments and understanding market context. These methods are key to effective risk management for all traders.
Why Traditional Stop-Losses Fail
Traditional price-based stop-losses can fail in volatile markets. A sudden price spike, common during flash crashes or earnings announcements, can trigger your stop even if the price quickly recovers. This forces you out of your position at the worst possible time, locking in an unnecessary loss. Furthermore, tight stops can lead to premature exits, while wide stops can result in substantial losses.
Context-Aware Stop-Loss Strategies
Experienced traders often employ more sophisticated, context-aware stop-loss strategies. These strategies adapt to changing market conditions, providing greater flexibility and protection. Your stop-loss isn’t static; it dynamically adjusts based on market behavior. Here are a few key techniques:
-
Volatility-Based Stops: These stops adjust based on the asset’s volatility. During volatile periods, the stop-loss widens to avoid being triggered by short-term price swings. In calmer markets, the stop-loss narrows.
-
Time-Based Exits: This strategy involves exiting a trade after a specific time, regardless of price. A day trader might exit all positions before market close, while a swing trader might exit after a few days or weeks. Check out the Time Stamps trading course- Trading with time and not price
-
Multi-Stage Risk Reduction: This involves gradually reducing your position as the trade moves in your favor. This locks in profits while allowing continued participation in potential further gains. You might sell half your position at your target price, then move the stop-loss for the remaining half to break-even.
Handling Challenging Market Scenarios
Certain market events require extra care when setting stop-losses, demanding dynamic strategies to mitigate large potential losses.
-
Overnight Gaps: Prices can gap significantly overnight, potentially triggering stops far below your intended exit. Guaranteed stop-loss orders can help, but usually come at a cost.
-
Earnings Announcements: Earnings releases often bring extreme volatility. Traders might avoid holding positions through earnings or significantly widen their stops.
-
Flash Crashes: These events can trigger stop-loss orders market-wide, causing cascading losses. Context-aware stops or even manual position management can be essential.
Case Studies: Stop-Loss Success and Failure
Real-world examples highlight the importance of proper stop-loss management. Some cases show how disciplined stop-loss use preserved capital during tough markets, enabling traders to capitalize on later recoveries. Others demonstrate the painful consequences of ignored or poorly placed stops, leading to significant losses. These experiences underscore the critical role of stop-loss orders in effective risk management. Understanding the nuances of stop-loss placement is a vital skill for handling market volatility and protecting your capital.
Leverage Technology To Automate Your Risk Controls
Modern traders have a powerful ally: technology. Using tech to enforce risk discipline isn’t just a good idea, it’s a game-changer. It transforms risk management from a theoretical exercise into a practical, automated system, providing a crucial advantage in today’s volatile markets. Let’s explore some of the tools that can revolutionize your risk management approach.
Software Solutions For Real-Time Risk Monitoring
Several software solutions offer real-time monitoring of vital metrics like position sizes, portfolio exposure, and correlation risks. These tools offer a continuous flow of data, enabling traders to make well-informed decisions swiftly. This proactive approach empowers traders to mitigate risks before they escalate.
For example, imagine holding a substantial position in a stock that suddenly experiences a surge in volatility. Real-time monitoring software can immediately alert you, allowing you to adjust your position or implement hedging strategies before significant losses occur.
This proactive approach is essential for effective risk management. Real-time monitoring also helps you identify and manage those hidden correlations within your portfolio, preventing seemingly diversified holdings from becoming concentrated risks during market downturns. This proactive stance is a cornerstone of successful trading.
Automating Alerts and Position Sizing
Automating key risk management tasks helps remove emotional biases from your decision-making process. Custom alerts are a great way to do this. These alerts can be set to notify you when a pre-defined risk threshold is breached, whether related to maximum drawdown, position size, or other critical metrics. Automated alerts ensure timely responses to risk events, preventing minor issues from snowballing into major problems.
Automated position-sizing calculators can also be incredibly helpful. They can help you determine the appropriate capital allocation for each trade, taking into account your overall risk tolerance and current market conditions. This removes the guesswork (and often emotional bias) from position sizing.
The evolution of risk management has been profoundly impacted by technology. The increasing use of risk management information systems (RMIS) allows for in-depth analysis of historical data and trends, helping traders make better informed decisions.
Scenario Analysis and Stress Testing
Professional trading operations often use scenario analysis and stress testing to prepare for unforeseen market shocks. This involves simulating various market scenarios, including extreme events, to understand their potential impact on the portfolio. By understanding how their portfolio might perform under different conditions, traders can develop contingency plans. This forward-looking approach enables them to anticipate and mitigate potential risks, fostering resilience during turbulent market periods. These tools help traders refine their strategies and improve risk-adjusted returns over time.
Comparing Risk Management Platforms
The right risk management platform depends on individual trading styles and needs. Some platforms are ideal for day traders, while others cater to swing traders or long-term investors.
Before making a decision, it’s crucial to compare available platforms. Consider their strengths, limitations, ease of use, integration with other trading tools, and the range of risk management features offered. Choosing the right platform is a critical step toward building a successful risk management strategy.
To help you compare some of the leading risk management tools, we’ve compiled the following table:
Risk Management Tools Comparison: A comparison of popular risk management software and tools available to traders
| Tool | Best For | Key Features | Price Range | User Level |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| TraderVue | Day and Swing Traders | Journaling, Analytics, Performance Tracking | $29-$179/month | Beginner to Advanced |
| TradingView | All Traders | Charting, Technical Analysis, Social Trading | Free-$59.95/month | Beginner to Advanced |
| NinjaTrader | Futures Traders | Order Flow, Advanced Charting, Backtesting | Free-$1099/month | Intermediate to Advanced |
| Risk Navigator | Portfolio Managers | Stress Testing, Scenario Analysis, Portfolio Optimization | Contact for Pricing | Advanced |
This table summarizes key features and pricing to help you choose the right tool for your specific needs. Remember to carefully research each platform to ensure it aligns with your trading style and provides the necessary functionality.
Portfolio Diversification That Actually Works
Diversification is a cornerstone of risk management for traders. However, building a truly resilient portfolio requires a deeper understanding than simply owning various assets. It involves understanding the relationships between those assets and their behavior under different market conditions. This means exploring the mathematics of correlation.

Unmasking Hidden Correlations
Many traders believe holding stocks across different sectors equates to diversification. However, seemingly unrelated assets can show strong correlations during market stress. For example, during the 2008 financial crisis, even traditional safe havens, like gold, initially fell alongside equities. This underscores the importance of recognizing hidden correlations that can surface during turbulent market periods. For further insights, explore this resource: How to master portfolio diversification.
Diversification Strategies of Professionals
Professional fund managers use a multi-pronged approach to diversification, spanning various areas:
-
Sectors: Instead of focusing on a single sector (like technology), they distribute investments across diverse sectors (healthcare, energy, consumer staples, etc.) to mitigate sector-specific risks.
-
Asset Classes: Diversification goes beyond stocks. Professional portfolios often incorporate bonds, real estate, commodities, and even alternative investments to blend assets with differing risk-return characteristics.
-
Strategies: Diversification also extends to trading strategies. Blending long-term investing with short-term trades, or fundamental analysis with technical analysis, creates a more robust portfolio.
Calculating and Monitoring Your Correlation Matrix
Understanding your portfolio’s correlation matrix is key for effective risk management. This matrix reveals the pairwise correlations between all assets in your portfolio. A correlation of +1 signals perfect positive correlation (assets move together), while -1 signifies perfect negative correlation (assets move inversely). A correlation near 0 suggests minimal relationship.
Regularly reviewing this matrix helps you adjust your portfolio and maintain balanced diversification. This entails identifying and potentially reducing highly correlated assets and adding negatively correlated ones.
Avoiding Diversification Pitfalls
A common trap is the illusion of diversification. Holding multiple stocks within the same sector may appear diverse, but the portfolio suffers if the sector underperforms. Another pitfall is neglecting rebalancing. Market fluctuations can shift portfolio weights over time, creating unintended risk concentrations. Regular rebalancing, achieved by selling over-performing assets and buying under-performing ones, maintains your desired asset allocation and risk profile.
Rebalancing Your Portfolio
A systematic rebalancing strategy is essential. Some traders rebalance at regular intervals (e.g., quarterly or annually), while others do so when asset weights stray from their target allocations. The chosen method hinges on individual risk tolerance and investment objectives.
By actively managing correlations, diversifying across asset classes and strategies, and routinely rebalancing, traders can construct more resilient portfolios. This diligent approach is fundamental for effective risk management and sustained success in the markets.
The Trader in the Mirror: Psychology of Risk Management
The most sophisticated risk management system is worthless without the discipline to follow it. This isn’t about software or spreadsheets; it’s about the human element. This section explores the psychological barriers that prevent traders from consistently applying risk management principles and provides strategies to overcome them.
Emotional Traps and Their Impact
Even with a perfect plan, emotions can derail a trader’s best intentions. Understanding these emotional pitfalls is the first step to mitigating their influence.
-
Loss Aversion: The pain of a loss is felt more strongly than the pleasure of an equivalent gain. This can lead to holding onto losing trades for too long, hoping they’ll recover. It can also cause prematurely exiting winning trades for fear of giving back profits.
-
Overconfidence: After a string of wins, traders can become overconfident. This can lead to increased risk-taking and ignoring predefined risk parameters. It often results in larger position sizes and neglecting stop-loss orders.
-
Revenge Trading: After a significant loss, the urge to “get even” with the market can be powerful. This emotional reaction often results in impulsive trades and further losses. Revenge trading is driven by a desire to recoup losses quickly, often involving greater risk-taking.
These are just a few of the emotional traps that can sabotage a trader’s risk management plan. Understanding the psychology behind risk can significantly improve your trading decisions. Building Emotional Resilience
Sticking to your risk management plan, especially during drawdowns and volatile markets, requires emotional resilience. This resilience is built over time through consistent practice and self-awareness.
-
Mindfulness and Meditation: Practicing mindfulness can help you become more aware of your emotional state. This allows you to react less impulsively to market fluctuations.
-
Journaling: Keeping a trading journal not only tracks your performance, but also your emotional responses to wins and losses. This self-reflection can reveal patterns and identify emotional triggers.
-
Positive Self-Talk: Replacing negative thoughts with positive affirmations can help build confidence and maintain a rational perspective during challenging market conditions.
Habit Formation for Automated Risk Management
Consistent risk management shouldn’t feel like a constant struggle; it should be an automatic response. This is achieved through habit formation.
-
Create a Checklist: Develop a pre-trade checklist that includes all your risk management parameters: position size, stop-loss level, and profit target.
-
Review Your Trades: Regularly review your trades, analyzing both successful and unsuccessful ones. Focus on how well you adhered to your risk management plan.
-
Visualize Success: Visualizing yourself successfully executing your trading plan, including adhering to your risk management rules, can reinforce positive habits.
You might be interested in How to master trading psychology for more in-depth strategies.
Creating a Culture of Risk Awareness
Successful trading operations prioritize risk awareness. This is achieved through clear communication, shared responsibility, and continuous learning. As an individual trader, you can apply these same principles:
-
Establish Clear Rules: Define your risk tolerance and create specific rules for position sizing, stop-loss placement, and overall portfolio exposure.
-
Regularly Review Performance: Conduct regular performance reviews, focusing on your risk-adjusted returns, not just overall profits.
-
Seek Mentorship: Connecting with experienced traders can provide valuable insights and help you develop a stronger risk management mindset.
By understanding your psychological biases, developing emotional resilience, and creating positive habits, you can transform risk management from a weakness into a strength. This mental discipline, combined with a robust risk management system, is the foundation of long-term trading success. Ready to elevate your trading? You can start with the Supply and Demand course, which blends technical with psychological elements to offer you a practical swing trading strategy.