What Is Algorithmic Trading? A Practical Guide
Algorithmic trading is simply a way of getting a computer program to place trades for you. The program follows a strict set of rules—a kind of recipe—based on price, timing, or how much is being traded. The whole point is to automate trading decisions, making them more efficient and, crucially, removing the emotional baggage that trips up so many human traders.
Think of it like a master chef following a complex recipe with superhuman speed. It hits every step with perfect precision and never, ever deviates from the plan.
The Core Concept of Automated Trading

At its heart, what people call "algo-trading" or "black-box trading" is all about swapping out human guesswork for cold, hard machine logic. Instead of a trader nervously hovering over the "buy" or "sell" button, an algorithm is constantly scanning the markets for the exact conditions it was built to find.
Once those conditions are met, boom—the algorithm pulls the trigger and executes the trade. This often happens in a fraction of a second, far faster than any human could react.
This process is a game-changer because it sidesteps the psychological traps that plague traders. Fear. Greed. Hope. An algorithm doesn't get rattled by a sudden market dip or chase a hot stock because of FOMO. It just follows its instructions, 24/7, without getting tired or emotional.
Why Automation Matters
The reasons traders and big financial institutions turn to algorithms are pretty straightforward, but incredibly powerful. They use them to:
- Get the best possible prices by analyzing market data faster than humanly possible.
- Slash transaction costs by placing orders strategically to avoid causing big price swings.
- Run incredibly complex strategies that would be a nightmare to manage by hand.
- Dodge emotional blunders by sticking to a pre-defined, backtested plan no matter what.
This whole approach leans heavily on sophisticated quantitative analysis in finance to spot opportunities and keep risk in check. It's a massive shift away from old-school, gut-feel trading.
Algorithmic trading is all about defining a repeatable, logical strategy and then letting technology execute it perfectly, every single time. It's the ultimate blend of math, computer science, and market expertise.
And this isn't just a tool for the Wall Street giants anymore. With technology becoming cheaper and more available, even retail traders are getting in on the action and building their own automated systems.
The market is exploding. The global algorithmic trading market was valued at USD 51.14 billion and is forecast to hit USD 150.36 billion, growing at a compound annual rate of 12.73%. You can dig into the full details in the Grand View Research report to see just how fast this space is moving.
The Journey from Ticker Tape to AI

To really get what algorithmic trading is today, we have to look back at where it came from. The idea of using tech for a market edge isn't new, but the way it's evolved is nothing short of dramatic. The story starts way before the internet, back in the 1970s.
This was the era of the first quantitative analysts, or "quants." These pioneers were using giant, room-sized computers to crunch market data and run what we'd now consider very basic models. Their goal was straightforward: find statistical patterns that human traders were missing. The methods were clunky and the tools were primitive, but they laid the foundation for everything to come.
The Rise of Electronic Markets
Things really started to pick up steam in the 1990s. The tech boom was in full swing, and with it came the rise of electronic trading. All of a sudden, trading floors filled with shouting traders started giving way to digital networks.
This shift was a massive game-changer. It meant orders could be sent and matched in seconds, not minutes, throwing the door wide open for faster and more sophisticated algorithms. The introduction of electronic communication networks (ECNs) in 1997 pushed things even further, letting big institutional players trade directly with each other and bypassing the traditional exchanges.
The core idea has always been the same: use technology to execute a predefined strategy. What changed was the speed and scale at which it could be done.
This technological leap set the stage for one of the most talked-about—and controversial—forms of automated trading.
High-Frequency Trading and the AI Revolution
By the 2000s, the race wasn't about seconds anymore; it was about milliseconds, then microseconds. This was the birth of High-Frequency Trading (HFT), a specialized branch of algorithmic trading where speed is the only thing that matters. HFT firms spend fortunes to co-locate their servers right next to an exchange's data centers, just to shave a few millionths of a second off their execution time.
Fast forward to today, and we're in another new phase, this time driven by Artificial Intelligence (AI) and machine learning. Modern trading algorithms are no longer just blindly following static "if this, then that" rules. Now, they can actually learn and adapt to changing market conditions on their own.
These AI-powered systems can sift through enormous, unstructured datasets—think news articles, social media chatter, satellite images—to try and predict where the market is headed next. They aren't just making old strategies better; they're inventing entirely new ways to trade, writing the latest chapter in this incredible technological story.
How Algorithmic Trading Systems Actually Work
So, how do these systems actually work? Let's pop the hood and see what makes them tick.
The easiest way to think about an algorithmic trading system is to picture a high-speed, fully automated factory. It takes in raw materials (data), processes them according to a very specific blueprint (the strategy), and spits out a finished product (a trade).
This whole operation, from spotting a market signal to executing the trade, happens in a blink of an eye, often without a human ever lifting a finger.
The Three Stages of an Automated Trade
At its heart, every algo trading system follows a simple, logical flow. It has to see what the market is doing, decide on a plan, and then act on that plan.
-
Data Input: The system is like a super-sensor, constantly drinking from a firehose of real-time market data. We're talking live price feeds, trading volumes, economic news—everything. These are the eyes and ears of the operation.
-
Strategy Logic and Signal Generation: This is the brain. The algorithm crunches all that incoming data and measures it against its programmed rules. The logic is often a straightforward “if-then” framework. For example, a rule might be: "IF a stock's price breaks above its 50-day moving average AND trading volume spikes by 20%, THEN generate a 'buy' signal."
-
Trade Execution: As soon as a signal is generated, the system instantly fires off the order to a brokerage or exchange. This is the hands of the operation, placing the buy or sell order with a speed and precision no human could ever match.
This clean, three-step process is the backbone of how these systems operate out in the wild.
The image below gives you a clear visual of this journey, from raw data to a finished trade.
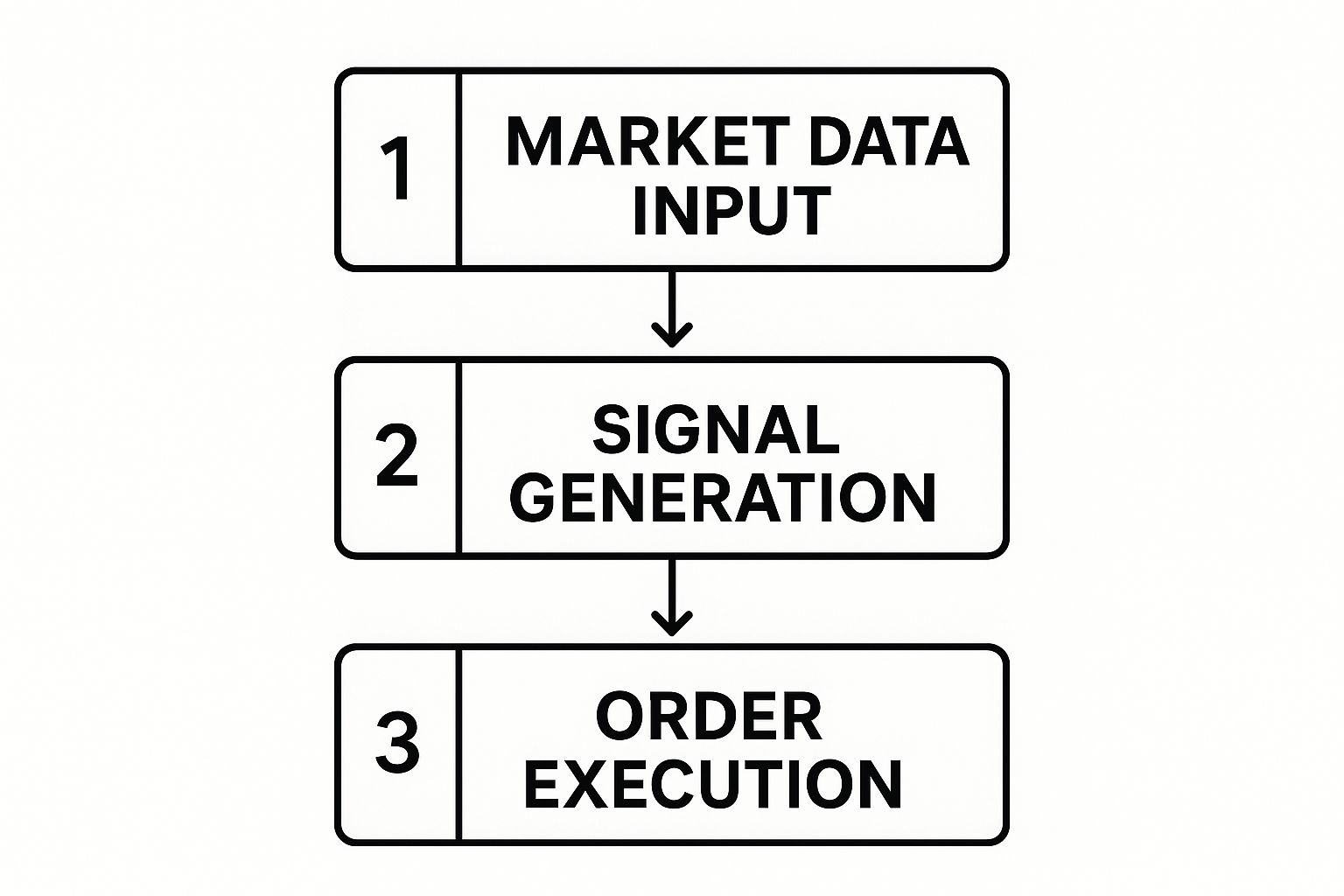
As you can see, it's a linear sequence. Each step triggers the next, which is what allows for those near-instant reactions to whatever the market throws at it.
The Role of Backtesting and Global Reach
Now, you don't just build an algorithm and let it run loose with real money. That would be insane.
Before any algorithm gets the green light, it goes through a brutal testing phase known as backtesting. This is where you run the strategy on historical market data to see how it would have performed in the past. It’s a make-or-break step to check the logic and spot any weaknesses before a single dollar is on the line.
If you want to go deeper, you can check out our own guide on how to backtest a trading strategy. It's absolutely critical to understand how to backtest trading strategies before deploying any kind of automated system.
The point of backtesting isn't just to see if a strategy could have been profitable. It’s about understanding how it behaves under all sorts of market conditions, from quiet, sideways markets to full-blown crashes.
The use of these systems isn't uniform across the globe, either. North America is currently the biggest player, thanks to its massive financial hubs and high trading volumes.
But the real story is the explosive growth in the Asia Pacific region, which is projected to expand at a rate of over 11% from 2025 onwards. It's a clear sign that traders and institutions worldwide are leaning more heavily on automation for better efficiency and access to markets.
Common Algorithmic Trading Strategies Explained

An algorithm is only as good as the strategy it’s told to execute. Think of it like a highly skilled pilot; that pilot is pretty useless without a flight plan. This is the "playbook" of automated trading—the core logic behind the most popular strategies driving the bots.
Each strategy is a different way of looking at the market and finding an edge. Understanding these core ideas is the key to grasping what algorithmic trading really is in practice, since they dictate exactly how these automated systems behave.
Riding Market Momentum
One of the most intuitive approaches out there is Trend-Following. The logic couldn't be simpler: if a stock is consistently climbing, the algorithm buys it, betting that the upward momentum will keep going. If an asset is in a clear downtrend, the algorithm will sell or short it.
Imagine a surfer trying to catch a wave. The goal isn't to predict when the wave will form, but to spot a strong one already in motion and ride it for as long as possible. The algorithm uses technical indicators like moving averages to confirm a trend’s direction and strength before jumping on board.
Betting on the Rebound
The polar opposite of riding a trend is Mean Reversion. This strategy is built on the belief that asset prices, over time, tend to snap back to their historical average or "mean." It operates like a stretched rubber band that eventually has to return to its resting state.
When a stock's price shoots up far above its average, a mean reversion algorithm might short it, betting on an eventual price correction. If the price plummets far below its average, the algorithm buys, anticipating a rebound back toward the middle.
A key concept here is that extreme price moves are often temporary. The algorithm’s job is to identify these overextensions and profit from the inevitable return to normalcy, turning market overreactions into opportunities.
Exploiting Tiny Price Gaps
Another powerful strategy is Arbitrage. This is all about finding tiny price differences for the exact same asset across different markets and profiting from the gap. For instance, if a company's stock is trading for $100.50 on the New York Stock Exchange and $100.52 on another exchange, an arbitrage bot will simultaneously buy on the cheaper exchange and sell on the more expensive one.
The profit on each trade is minuscule—just two cents, in this case—but when you multiply that by millions of shares, it adds up to serious money. This requires immense speed, as these price gaps often only exist for fractions of a second.
The Need for Speed: High-Frequency Trading
This brings us to the supercharged world of High-Frequency Trading (HFT). HFT isn't really a single strategy on its own; it's more of a method that uses incredible speed to execute other strategies, like arbitrage, thousands of times per second. To dig deeper, you can check out our complete guide on high-frequency trading explained.
This global obsession with speed is all about getting better order execution and providing instant liquidity to the markets. The demand is so high that the global algorithmic trading market, valued at USD 3.28 billion, is projected to nearly double to USD 6.05 billion, largely driven by the hunger for these low-latency operations. You can discover more insights about the market growth from Coherent Market Insights.
Understanding the Benefits and Inherent Risks
Automated trading brings incredible power to the table, but that power comes with some serious, often overlooked, risks. You absolutely have to understand both sides of this coin before even thinking about letting an algorithm trade for you. The benefits are definitely compelling, and they offer a sharp edge over old-school human trading in a few key ways.
But here's the catch: the downsides can be catastrophic if you don't manage them properly. A powerful tool can quickly become a massive financial liability. A balanced perspective isn't just helpful; it's essential.
The Clear Advantages of Automation
The most obvious benefit is just pure, blazing-fast execution speed. An algorithm can spot an opportunity and place a trade in microseconds—a speed that's literally impossible for a human. This kind of speed is make-or-break for strategies like arbitrage, where tiny price differences might only exist for the blink of an eye.
Beyond just being fast, algorithms bring a level of accuracy and discipline that humans just can't match. They execute a strategy perfectly, every single time, without any emotional baggage getting in the way.
- Eliminates Emotional Decisions: Algorithms don't feel fear, greed, or hesitation. This takes out the single biggest point of failure for most manual traders and makes sure the trading plan is followed to the letter, no exceptions.
- Enables Rigorous Backtesting: Before you risk a single dollar of real money, you can test a strategy against years of historical data. This process, known as backtesting, gives you a crucial look at how your strategy would have held up through all sorts of market weather.
- Operates Around the Clock: An automated system can keep an eye on global markets 24/7. It catches opportunities that a human trader, who needs to sleep and take breaks, would inevitably miss.
The core advantage here is replacing human fallibility with machine-like consistency. An algorithm executes a predefined, tested plan with perfect discipline, which is the cornerstone of any long-term trading success.
The Hidden Dangers and Critical Risks
For all its advantages, the world of algorithmic trading is full of pitfalls. The same speed that creates opportunities can also magnify your losses at a terrifying rate. A tiny coding error or a simple system glitch can lead to a financial disaster in just a few seconds.
One of the biggest technical risks you'll face is overfitting. This is what happens when a strategy is tuned so perfectly to past data that it looks amazing in backtests but completely falls apart in a live market. The model has essentially memorized the "noise" from old data instead of learning a real, repeatable market pattern.
And don't underestimate the complexity. Building, testing, and maintaining a trading system demands some serious technical skill in programming, data analysis, and market infrastructure. A simple bug, a lost internet connection, or an unexpected market event can have severe consequences. These systems are not "set and forget"—they require constant monitoring and a deep understanding of how they work to prevent a total meltdown.
Your Guide to Getting Started
Dipping your toes into the world of algorithmic trading can feel a bit overwhelming. But like any complex skill, it gets a lot simpler when you break it down into manageable steps.
You don't need to be a Wall Street quant to get started, but you absolutely need the right toolkit and a clear roadmap.
Think of it this way: every algorithmic trading system, from the most basic to the wildly complex, stands on three essential pillars.
- A Brokerage with API Access: The Application Programming Interface (API) is just a fancy term for the digital handshake that lets your trading program talk directly to your broker to execute trades. Most modern brokers offer this now.
- A Solid Data Source: Your algorithm is completely blind without good market data. This could be live, real-time data for active trading or historical data for the all-important backtesting phase.
- A Programming Language: While you have options, Python has pretty much become the king of the hill for traders. Its powerful libraries for data crunching and analysis make it the go-to for beginners and seasoned pros.
Choosing Your Starting Path
Once you have the basic tools in mind, there are really two main paths you can take. Your choice boils down to your comfort level with technology and how much hands-on control you want.
One popular route is to use a dedicated algorithmic trading platform. These platforms are designed to be user-friendly, letting you build, test, and launch strategies with minimal coding. They handle all the messy backend stuff so you can focus on the trading logic itself.
The other path is to build a custom system from scratch. This gives you ultimate flexibility and control, but it's a heavy lift, requiring serious programming and system design skills. That said, even simple tools can teach you a lot; for instance, if you want to create an automated trading system in Excel, it's a fantastic way to grasp the core logic without getting lost in complex code.
Whichever path you choose, the golden rule is always the same: start small and test everything. Begin with a simple idea, backtest it until you're tired of looking at it, and only then consider putting real money on the line. This is a marathon, not a sprint, and it's all about continuous learning and refinement.
Frequently Asked Questions
Diving into the world of algorithmic trading always stirs up a few questions, especially if you're just getting your feet wet. Getting straight answers is the first step to feeling confident about how these systems really work in today's markets.
Let's tackle some of the most common queries traders have about letting code do the heavy lifting.
Is Algorithmic Trading Legal?
Yes, algorithmic trading is completely legal and is a fundamental, regulated part of modern financial markets.
The lines get crossed, however, when strategies are built specifically to manipulate the market. Things like "spoofing"—placing big orders you have no intention of filling just to trick others—are illegal and will land you in hot water with regulators. It all comes down to the intent behind your strategy and whether it plays by the rules of fair trading.
Can I Use Algorithmic Trading as a Small Investor?
Absolutely. What was once the exclusive playground for big institutions is now wide open to retail investors.
Many online brokers offer APIs (Application Programming Interfaces), which are basically just a way for you to plug your own custom trading algorithms directly into their platform. Services like Alpaca or QuantConnect have even popped up to give individual traders the infrastructure to build, test, and run their own bots. The barrier to entry has never been lower.
The rise of accessible APIs and cloud-based platforms has democratized algorithmic trading, making it a viable tool for individual traders who are willing to learn the necessary technical skills.
What Is the Best Programming Language for Algorithmic Trading?
For most people, the answer is Python. It's the undisputed champion for individual traders and quants, and for good reason. It has an incredible ecosystem of libraries for data analysis (like Pandas and NumPy) and machine learning (like Scikit-learn) that make building and backtesting strategies incredibly efficient.
Now, if you're in the high-frequency trading game where every single microsecond is the difference between profit and loss, you'll see firms using C++ for its raw, unadulterated speed. But for just about everyone else starting out, Python is the perfect place to begin.
Ready to master the markets without relying on complex algorithms? At Colibri Trader, we teach a powerful, price-action based approach that works in any market condition. Start your journey and transform your trading today.