Managing Trading Risk: Proven Strategies That Actually Work
Understanding Today's Complex Trading Risk Environment
The trading world has grown significantly more complex, making traditional risk management methods inadequate. Interconnected global markets, high-frequency algorithmic trading, and shifting geopolitical tensions all contribute to this increased complexity. These factors create new levels of volatility and uncertainty, demanding a more sophisticated approach to risk management.
Core Risk Types in Modern Trading
Effective risk management begins with understanding potential problems. Four core risk types can greatly impact trading outcomes:
-
Market Risk: This stems from price swings in the asset being traded. For instance, a sudden drop in a stock's value due to a disappointing earnings report can result in substantial losses.
-
Credit Risk: This involves the possibility of losses if another party fails to meet its contractual obligations. This can happen in derivatives trading or over-the-counter (OTC) markets.
-
Liquidity Risk: This is the risk of being unable to buy or sell an asset quickly enough to prevent a loss. This is especially challenging during periods of market instability.
-
Operational Risk: This covers risks stemming from internal processes, systems, or human error. Issues like a flawed trading algorithm or a rogue trader can lead to substantial operational losses.
Let's explore these different risk types in more detail to better understand their characteristics and how they might affect trading decisions.
To provide a visual overview of some common mitigation techniques, the following infographic demonstrates the use of stop-loss orders, position sizing, and diversification.
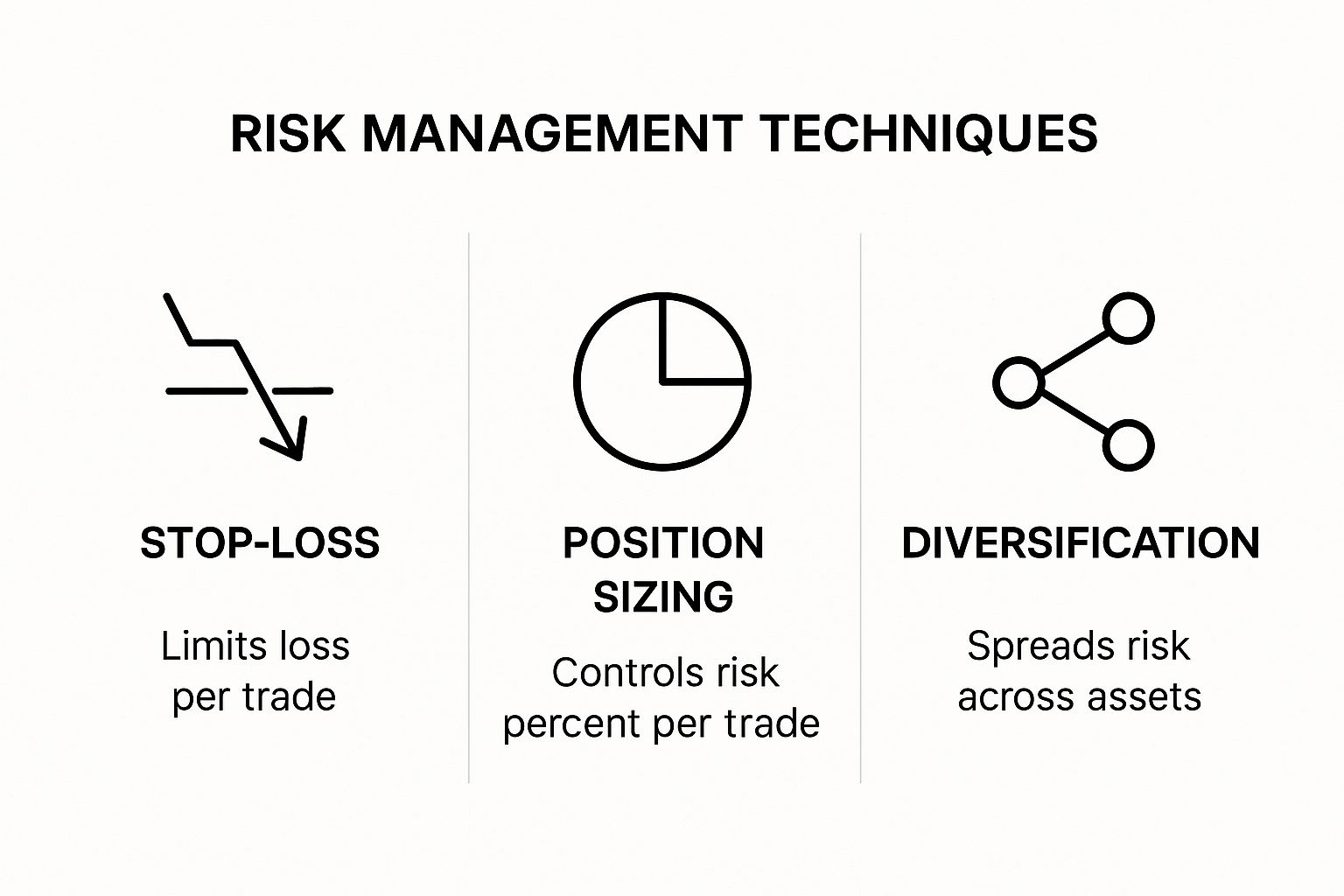
As illustrated, combining these core techniques builds a strong risk management framework. Stop-loss orders cap individual trade losses, position sizing manages overall portfolio exposure, and diversification spreads risk across different assets. The increasing need for these techniques is reflected in the growth of the risk management market. Valued at $13.5 billion in 2024, it is projected to reach $38.9 billion by 2033, exhibiting a 12.48% CAGR. Learn more about this expanding market: https://www.imarcgroup.com/risk-management-market
To further clarify the nuances of trading risks, the following table provides a breakdown of different risk types:
"Types of Trading Risks and Their Key Characteristics"
A comprehensive comparison of major trading risk categories, their typical impact levels, and primary mitigation approaches.
| Risk Type | Definition | Impact Level | Primary Mitigation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Market Risk | Arises from price fluctuations in the underlying asset. | High | Diversification, stop-loss orders, hedging |
| Credit Risk | Potential for losses if a counterparty fails to meet its obligations. | High | Due diligence, netting agreements, collateral |
| Liquidity Risk | Risk of not being able to buy or sell an asset quickly enough to avoid a loss. | Medium to High | Limit orders, position sizing, market depth analysis |
| Operational Risk | Risks related to internal processes, systems, or human error. | Medium to High | Robust internal controls, automated systems, staff training |
This table summarizes the key characteristics of each risk, highlighting their potential impact and primary mitigation strategies. Understanding these factors is crucial for developing a comprehensive risk management plan.
Adapting to Market Realities
Traditional, static, rule-based risk management systems struggle to adapt to sudden market shifts. Traders must adopt more dynamic and adaptable approaches. This involves constant market monitoring, adjusting trading strategies, and using sophisticated risk management tools. By being proactive and flexible, traders can better manage the complexities of today's markets and protect their capital.
Building Your Personal Risk Management System
A robust risk management system is essential for navigating the often turbulent waters of trading. Instead of relying on generic advice, successful traders create a personalized approach. This tailored system considers individual trading styles, goals, and, importantly, risk tolerance. It involves understanding your comfort levels with potential losses, using strict position sizing rules, and having contingency plans in place.
Defining Your Risk Tolerance
Risk tolerance isn't a fixed number; it's a personal evaluation of how much you're comfortable losing on a single trade or a series of trades. This assessment should consider your financial situation, trading goals, and your psychological comfort level with risk. For example, a newer trader with a smaller account might have a lower risk tolerance than a seasoned trader with more capital. Defining realistic limits helps you trade without undue fear or anxiety.
Implementing Position Sizing Rules
Position sizing is a critical component of risk management. It dictates how much capital to allocate to each trade, protecting your account from substantial losses. This involves calculating a percentage of your account to risk on any given trade. For instance, risking 1% per trade on a $10,000 account means you can afford a $100 loss. This method helps limit losses and preserves capital. Read also: How to master money management in trading.
Developing Contingency Plans
Market conditions are constantly changing. Therefore, contingency plans are crucial for handling unexpected events. These plans outline predefined actions to take if a trade moves against you. This could involve setting specific exit points or adjusting stop-loss orders as market volatility fluctuates. Contingency planning helps traders remain disciplined and prevents emotional decisions during stressful market situations.
Utilizing Risk Management Tools
Several tools can enhance your risk management system. Value at Risk (VaR) calculates potential losses over a specific timeframe, offering a statistical measure of risk. Stress testing your portfolio simulates its performance under adverse market conditions, like a crash or volatility spike. Scenario planning explores the potential impact of different events, helping you prepare for various outcomes.
The growing importance of risk management is evident in its market growth. Driven by increased regulatory requirements and economic instability, this market is expanding rapidly. In 2024, it was valued at $12.09 billion, projected to reach $13.78 billion by 2025, a 14.0% CAGR. Learn more: https://www.thebusinessresearchcompany.com/report/risk-management-global-market-report.

By implementing these strategies and tools, you build a personalized risk management system. This system helps you navigate market fluctuations and allows you to confidently make informed trading decisions. This proactive approach is key to protecting capital, achieving your trading goals, and building long-term success.
Staying Ahead of Geopolitical Market Disruptions
Geopolitical events can significantly impact financial markets, presenting both risks and opportunities for traders. Understanding these dynamics is crucial for effective risk management. Ignoring geopolitical factors can lead to unexpected losses, while recognizing and adapting to them can enhance trading strategies. This involves identifying potential geopolitical risks, assessing their potential impact, and developing strategies to mitigate those risks.
Recognizing Geopolitical Risks
Identifying potential geopolitical risks requires constant monitoring of global events. This includes following news sources, political analysis, and economic indicators.
- Escalating tensions between countries
- Changes in government policies
- Social unrest
These events can signal potential market disruptions and trigger volatility in various asset classes, including currencies, commodities, and stocks. When building your personal risk management system, understanding different levels of documentation is important. For more insight into structured documentation, explore resources like process SOPs and work instructions.
Assessing Market Impact
Not all geopolitical events have the same impact on markets. Analyzing which events truly move markets versus those causing short-term noise is essential. Consider the potential impact on:
- Supply chains
- Trade relationships
- Investor sentiment
Geopolitical risk is a key factor in trading risk management, impacting market volatility and asset prices. The BlackRock Geopolitical Risk Indicator (BGRI), updated as recently as April 2025, illustrates how these events create shocks in global asset markets.
Developing Mitigation Strategies
Once potential geopolitical risks are identified, traders can develop appropriate mitigation strategies. This might involve:
- Hedging strategies
- Diversifying portfolios
- Adjusting position sizes
For instance, if a trader anticipates a currency devaluation due to political instability, they might reduce their exposure to that currency or use options contracts to hedge against potential losses. Another approach is scenario planning, where traders analyze potential outcomes and develop strategies to handle each. This proactive approach is crucial for managing trading risk in an increasingly interconnected world.
Leveraging Technology For Smarter Risk Control

Modern risk management in trading requires more than just gut feelings. It requires using technology to protect your capital. This section explores how technology is changing the game of trading risk management. From AI-powered insights to automated trade execution, these tools offer traders powerful new capabilities.
AI and Machine Learning in Risk Management
Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning are changing the way traders identify and reduce risks. These technologies can analyze massive datasets to find patterns and anomalies that a human might miss.
For example, AI can detect subtle shifts in market sentiment or find correlations between seemingly unrelated assets. This provides early warnings of potential market disruptions, allowing traders to adjust their strategies and protect their capital. Machine learning algorithms can also analyze past trading data to identify behavioral biases that may lead to excessive risk-taking.
Automated Risk Management Systems
Automated systems are essential for managing trading risk, especially in fast-paced markets. Automated stop-loss orders automatically execute trades to limit potential losses when a security's price falls below a set level.
Similarly, algorithmic trading systems can dynamically adjust position sizes and hedging strategies based on real-time market conditions. These automated controls can react much faster than a human, a key advantage during periods of high volatility. This speed and efficiency significantly improve risk management capabilities. However, it's important to remember that even automated systems need regular oversight and adjustment.
Practical Applications for Different Traders
The advantages of technology in risk management apply to traders of all experience levels and budgets. While advanced AI-powered platforms can be expensive, there are plenty of affordable or free tools available.
Basic charting software often includes features like automated stop-loss orders and backtesting capabilities. Many brokers also offer risk management tools integrated within their trading platforms.
Evaluating Technology and Avoiding Hype
It's crucial to distinguish genuinely useful technology from marketing hype. Not every new tool will drastically improve your results. When evaluating new risk management technology, focus on practical applications and how it directly addresses your specific trading needs.
For example, while a complex AI system might seem appealing, a simple automated stop-loss order might be more suitable for a day trader. The most effective technology is the technology you understand and can actually use well.
Choosing the Right Tools for You
Consider factors like your trading style, budget, and technical skills. The following table, "Risk Management Technology Comparison," analyzes popular risk management tools, their features, costs, and suitability for different trader types. It provides a helpful overview for making informed decisions.
Risk Management Technology Comparison
| Tool/Platform | Key Features | Cost Range | Best For | Complexity Level |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Charting Software with Basic Risk Management | Automated Stop-Loss, Backtesting | Free – $$ | Beginners, Intermediate Traders | Low |
| Broker-Provided Risk Management Tools | Real-Time Monitoring, Alerts | Included with Brokerage Account | All Traders | Low – Medium |
| Specialized Risk Management Platforms | AI-Powered Analysis, Algorithmic Controls | $$$ – $$$$ | Advanced Traders, Institutions | High |
By understanding the available options and focusing on your specific needs, you can make informed decisions about which technologies will truly improve your risk management process. Choosing the right tools can make a significant difference in your overall trading performance.
Mastering The Mental Game Of Risk Management

Market volatility is a given in trading, but your biggest challenge isn't external; it's internal. It's about managing your own psychology. This section explores the mental pitfalls that can derail even the most carefully constructed risk management plans, leading to costly mistakes and substantial losses. Mastering this mental game is just as vital as understanding technical analysis.
Identifying Behavioral Biases
Several behavioral biases can negatively impact trading decisions and risk management. Overconfidence, for instance, can fuel excessive risk-taking and a tendency to dismiss warning signs. Traders might overestimate their own skills while simultaneously underestimating the inherent risks of the market.
Revenge trading is another significant hurdle. Fueled by the emotional sting of losses, traders often attempt to recoup their funds quickly, leading to even greater losses. This impulsive behavior can rapidly deplete trading capital.
Loss aversion, the tendency to feel the pain of a loss more acutely than the pleasure of a gain, also plays a role. It can cause traders to cling to losing positions, hoping for a turnaround, while prematurely closing winning trades out of fear. These biases are detrimental to long-term trading success. For practical advice, check out our guide on How to master your trading psychology.
Maintaining Discipline Under Pressure
Maintaining discipline and emotional control during volatile market conditions is essential for effective risk management. Fear and greed can cloud judgment, leading to impulsive decisions that deviate from your trading plan. Fear may cause you to exit a winning trade too early, while greed can lead you to hold onto a losing trade for too long.
Developing Mental Resilience
Building mental resilience is an ongoing process that requires self-awareness and consistent practice. It involves objectively assessing your trading performance, pinpointing weaknesses, and developing strategies to address them. Here are a few helpful techniques:
-
Journaling your trades: Documenting your emotional state during each trade can help you identify recurring patterns and emotional triggers.
-
Practicing mindfulness and meditation: Techniques like deep breathing can help you maintain calm during stressful trading situations.
-
Seeking feedback from experienced traders or mentors: An outside perspective can often reveal blind spots and highlight areas for improvement.
By acknowledging and addressing these psychological factors, traders can significantly enhance their decision-making process and improve their risk management. The most successful traders recognize the importance of psychology alongside technical and fundamental analysis. They understand that managing emotions is key to consistent, long-term success. This approach fosters more rational trading decisions, helping traders remain focused on their overall goals. Ultimately, mastering the mental game distinguishes consistent winners from those who struggle to manage risk effectively.
Getting Position Sizing And Diversification Right
Successfully navigating the complexities of trading requires a keen understanding of risk management. Two crucial elements of this are position sizing and diversification. These strategies work in tandem to protect your capital and potentially boost your returns. Position sizing helps you determine how much to invest in each trade, while diversification spreads your risk across multiple assets.
Optimizing Position Sizing for Maximum Growth
Position sizing involves more than just risking a fixed percentage, say 2%, on every trade. It's about strategically allocating capital based on your specific goals and risk tolerance. There are various methods to determine optimal position size, each with its own set of advantages and disadvantages.
-
Fixed Fractional: This method involves allocating a fixed percentage of your capital to each trade, irrespective of market conditions. Its simplicity makes it particularly attractive for beginners.
-
Volatility-Based: This approach adjusts position sizes based on the volatility of the asset. More volatile assets receive smaller allocations, while less volatile assets receive larger allocations. This helps manage overall portfolio risk.
-
Kelly Criterion: A more complex method, the Kelly Criterion aims to maximize long-term growth by factoring in the probability of winning and the potential payoff of a trade. While potentially highly profitable, it also carries higher risk if calculations are incorrect.
For instance, using the fixed fractional method with a 2% allocation on a $10,000 account means risking $200 per trade. With a volatility-based approach, a trader might risk less than $200 on a volatile stock and more on a stable bond.
Diversification Strategies That Truly Reduce Risk
Effective diversification goes beyond simply owning a variety of assets. It involves understanding the relationships between those assets, considering sector rotation, and even looking at geographic distribution.
-
Correlation Analysis: This involves understanding how different assets move in relation to one another. A well-diversified portfolio ideally contains assets with low or negative correlations. This helps mitigate losses by ensuring that not all assets decline simultaneously.
-
Sector Rotation: This strategy involves strategically shifting investments between different sectors of the economy based on market cycles. For example, rotating into defensive sectors (like utilities or consumer staples) during economic downturns can help protect your portfolio.
-
Geographic Diversification: Investing across different countries or regions can help reduce the impact of country-specific economic or political risks. This can help stabilize returns by reducing exposure to any single country’s economic performance.
By implementing these diversification strategies, investors can build more resilient portfolios. This resilience helps weather market fluctuations and protects against unforeseen events.
Balancing Concentration and Diversification
Finding the optimal balance between concentrated positions and broad diversification is crucial. Too much concentration amplifies risk, while excessive diversification can dilute potential returns. The ideal balance depends on factors like individual risk tolerance, investment timeframe, and market outlook. Regularly re-evaluating and adjusting your diversification strategy, as markets and personal circumstances change, is essential for effective risk management.
Monitoring And Evolving Your Risk Strategy
Managing trading risk isn't a set-it-and-forget-it task. It's a continuous cycle of monitoring, evaluation, and adjustment. It's like steering a ship – you're always correcting your course based on the changing weather, currents, and your final destination. This section explains how to create a dynamic system for managing your trading risk, one that tracks your exposure, alerts you to potential problems, and helps you navigate shifting market conditions.
Establishing Real-Time Monitoring Systems
The foundation of a dynamic risk management system is real-time monitoring. This means tracking key metrics that offer insights into your risk exposure. Crucial metrics include:
- Portfolio Volatility: This measures how much your portfolio's value fluctuates, giving you a quick overview of your overall risk.
- Margin Levels: Carefully watching your margin account helps you avoid margin calls and forced liquidations.
- Drawdowns: Monitoring drawdowns, the peak-to-trough decline in your portfolio over a specific time, helps you understand how much your portfolio could potentially decrease in value.
- Maximum Loss Potential: Knowing the maximum potential loss on any given trade helps you stay within your pre-defined risk tolerance.
These metrics provide a constant, real-time view of your risk profile. This allows you to act quickly if necessary. Think of your car's dashboard – these metrics are like your essential gauges, constantly providing feedback on the health of your trading "vehicle.”
Conducting Regular Risk Assessments and Backtesting
Regular risk assessments and backtesting are critical for a proactive approach to risk management. Think of it as preventative maintenance for your trading strategy. Risk assessments involve reviewing your entire trading system, looking for potential vulnerabilities and areas for improvement. For example, are your position sizes still appropriate for your account size and risk tolerance? Are your stop-loss orders correctly placed? These regular check-ups help identify weak points before they become expensive problems.
Backtesting involves testing your strategy against historical data. This shows you how your system would have performed in different market environments. This historical perspective can help you identify potential flaws and improve the robustness of your strategy. Backtesting provides data-driven insights to refine and optimize your trading approach.
Adapting to Changing Market Dynamics
Markets are constantly changing, and your risk management strategy must adapt. This means understanding how to adjust your approach during different market phases. For example, during periods of high volatility, you might reduce your position sizes or tighten your stop-loss orders. During periods of low volatility, you might consider increasing your exposure. Learn more in our article about How to master risk management for traders.
Maintaining Risk Logs and Post-Trade Analysis
Keeping a detailed risk log helps you track the risk parameters of every trade: entry and exit points, stop-loss levels, position sizes, and the reasoning behind each trade. This log becomes a valuable tool for post-trade analysis, helping you understand what works and what doesn't. Honest post-trade analysis is crucial for learning from your mistakes and improving your trading. This involves reviewing both winning and losing trades to identify strengths and weaknesses in your decision-making.
By continually refining your risk management processes, you not only protect your capital but also improve your long-term trading performance. This ongoing adaptation is the key to a sustainable and successful trading career. Ready to improve your trading? Visit Colibri Trader and explore our educational resources designed to help you master trading.