Top Beginner Trading Strategies for 2025: Start Today!
Diving into the world of trading can feel overwhelming. With endless charts, jargon, and fast-moving prices, it is easy to feel lost before you even begin. The secret to success is not a magic formula but a solid foundation built on proven, understandable methods. This guide is designed to cut through the noise, offering 10 practical and actionable beginner trading strategies that prioritize clarity and consistency over needless complexity. We will move beyond vague advice and provide a clear roadmap that focuses on price action and disciplined execution, principles at the core of successful trading.
This listicle serves as a toolkit, equipping you with the fundamental techniques needed to analyze market behavior and make informed decisions. We will explore several key approaches, including:
- Long-term investment methods like Buy and Hold and Dollar-Cost Averaging (DCA).
- Active trading techniques such as Trend Following and Support and Resistance Trading.
- Indicator-based systems like the Moving Average Crossover Strategy.
Whether you aim to invest for the long term or make your first day trade, these strategies will provide the essential framework you need to navigate the markets with confidence. Let's explore the fundamental approaches that can help you transform from a market spectator into a capable participant.
1. Buy and Hold Strategy
Often considered more of an investment philosophy than an active trading technique, the Buy and Hold strategy is one of the most accessible and proven beginner trading strategies available. The core principle is simple: purchase assets like stocks or exchange-traded funds (ETFs) and hold them for a long period, typically five years or more. This approach is built on the historical evidence that, despite short-term volatility and market crashes, financial markets tend to increase in value over the long term.
Legendary investor Warren Buffett famously championed this method, focusing on acquiring fundamentally strong companies and holding them for decades. For a newcomer, this strategy removes the stress of trying to time the market, which is a common and costly mistake. Instead of reacting to daily news and price swings, the focus shifts to long-term growth and the power of compounding.
How to Implement Buy and Hold
Getting started is straightforward. A great entry point is through diversified index funds or ETFs, such as one tracking the S&P 500. This instantly gives you a stake in hundreds of leading U.S. companies.
- Set up automatic investments: Schedule regular, automatic contributions from your bank account to your brokerage account. This practice, known as dollar-cost averaging, helps you buy more shares when prices are low and fewer when they are high.
- Reinvest all dividends: Most brokerages allow you to automatically reinvest dividends paid out by your holdings. This is a critical step for maximizing compound growth, as your earnings start generating their own earnings.
- Review, don't react: A buy and hold portfolio doesn't mean "set it and forget it" entirely. Plan to review your holdings annually to ensure they still align with your financial goals, but resist the urge to check performance daily or sell during a market downturn.
The following infographic highlights the foundational pillars of this strategy for quick reference.
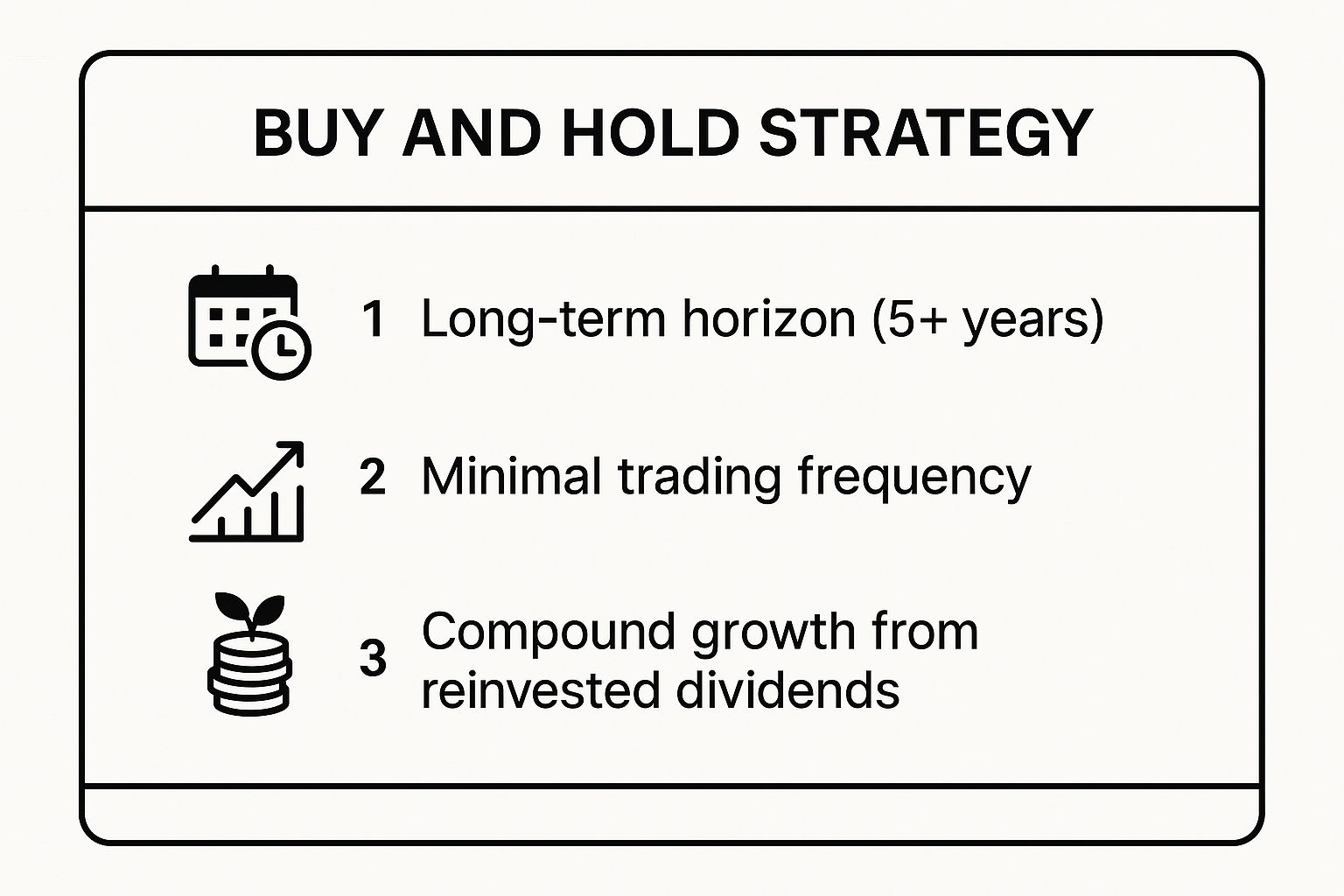
These key takeaways underscore that the strategy's success relies on patience, minimal intervention, and leveraging compound interest over time. By focusing on a long-term horizon, you allow your investments the necessary time to recover from downturns and grow substantially.
2. Dollar-Cost Averaging (DCA)
A powerful companion to long-term investing, Dollar-Cost Averaging (DCA) is one of the most practical and disciplined beginner trading strategies. The core idea involves investing a fixed amount of money at regular intervals, such as monthly or weekly, regardless of the asset's price. This systematic approach smooths out the average purchase price over time, mitigating the risk of investing a large lump sum at a market peak.
This strategy is celebrated by figures like John Bogle and Burton Malkiel for its ability to remove emotion and guesswork from investing. By committing to a consistent schedule, you automatically buy more shares when prices are low and fewer when they are high. This removes the pressure of trying to perfectly time the market, a common pitfall for newcomers. The systematic nature of DCA is a key component of effective decision-making under uncertainty, allowing you to build a position methodically.

How to Implement Dollar-Cost Averaging
Implementing DCA is simple and can be almost entirely automated, making it an excellent hands-off strategy. It works exceptionally well for building positions in broad-market index funds, ETFs, or even individual assets over time.
- Automate your contributions: The most effective way to practice DCA is to set up automatic transfers from your bank account to your brokerage account on a recurring basis. This enforces discipline and consistency.
- Start with a sustainable amount: Choose an investment amount that fits comfortably within your budget. It's better to start with a smaller, sustainable amount (e.g., $100 per month) than an ambitious one you might have to pause.
- Stay the course: The main benefit of DCA is realized by sticking to the plan through both market highs and lows. Resist the temptation to stop investing during a downturn, as these are the times your fixed investment buys more shares.
These steps emphasize that DCA's strength lies in consistency and discipline. By focusing on a regular investment schedule rather than market timing, you reduce volatility's impact and can potentially lower your overall average cost per share, setting a solid foundation for long-term portfolio growth.
3. Trend Following Strategy
One of the most intuitive and popular beginner trading strategies is Trend Following. This method operates on the principle that assets moving in a specific direction will continue to do so for some time. Instead of predicting tops or bottoms, traders simply identify an existing trend and ride it, buying an asset as it rises (uptrend) or short-selling as it falls (downtrend). The core idea is captured in the classic trading adage: "the trend is your friend."
This approach was famously and successfully implemented by Richard Dennis and his group of novice traders, known as the "Turtle Traders," who proved that successful trading could be taught and systematized. The strategy removes the need for complex market forecasting, focusing instead on reacting to established price movements. To delve deeper into how to identify and trade these movements, you can learn more about price action trading.

How to Implement Trend Following
Implementing this strategy involves using technical indicators to confirm a trend's direction and strength. A common starting point is using moving averages, such as identifying when a 50-day moving average crosses above a 200-day moving average, signaling a potential long-term uptrend.
- Confirm the trend: Use at least two different indicators to confirm a trend before entering a trade. For example, combine a moving average crossover with the Relative Strength Index (RSI) to avoid false signals.
- Set strict stop-losses: The trend will eventually end. A crucial component of this strategy is placing a stop-loss order to protect your capital when the market inevitably reverses.
- Start with longer timeframes: Trends are generally more reliable and clearer on longer timeframes like daily or weekly charts. This reduces market "noise" and provides stronger signals for beginners.
- Practice with position sizing: Never risk more than a small percentage (e.g., 1-2%) of your trading capital on a single trade. Proper position sizing ensures you can withstand a series of small losses while waiting for a large, profitable trend.
4. Support and Resistance Trading
A cornerstone of technical analysis, Support and Resistance Trading is one of the most fundamental and widely used beginner trading strategies. This method involves identifying key price levels on a chart where the price has historically struggled to move past. A "support" level acts as a price floor where buying pressure tends to overcome selling pressure, causing the price to bounce up. Conversely, a "resistance" level acts as a price ceiling where selling pressure overwhelms buying pressure, causing the price to stall or reverse.
Pioneered by early market technicians like Charles Dow and Jesse Livermore, this strategy helps traders visualize supply and demand dynamics directly on a price chart. For a beginner, mastering the art of identifying these zones provides a clear framework for making trading decisions, such as buying near support in an uptrend or selling near resistance in a downtrend.
How to Implement Support and Resistance Trading
To apply this strategy, you must first learn how to draw these levels on a chart. This skill improves with practice and can be enhanced by looking for specific confirmations before entering a trade.
- Identify key levels: Look for at least two or three historical price points where the asset has reversed or paused. The more times a level is tested and holds, the stronger it is considered.
- Use volume for confirmation: A strong bounce off a support level accompanied by high trading volume adds significant confirmation to the validity of that level. Low volume suggests a weaker move.
- Set stop-loss orders: Place your stop-loss just below the support level when buying, or just above the resistance level when selling. This helps manage risk if the level breaks.
- Combine with other indicators: Enhance your analysis by using other tools like moving averages or candlestick patterns to confirm the signals at these critical price zones.
For those looking to deepen their understanding, you can learn more about how to read stock charts on colibritrader.com. By identifying these price barriers, traders can set precise entry and exit points, creating a high-reward, low-risk trading setup. This makes it an invaluable skill for anyone new to the markets.
5. Moving Average Crossover Strategy
One of the most popular and visual beginner trading strategies, the Moving Average Crossover strategy, uses indicators to identify momentum shifts and potential entry or exit points. The core idea involves plotting two moving averages (MAs) of different time periods on a chart. A trading signal is generated when the shorter-term MA crosses over or under the longer-term MA. This crossover suggests a potential change in the trend's direction.
A "golden cross" occurs when a shorter-term MA (like the 50-day) crosses above a longer-term MA (like the 200-day), signaling a potential uptrend and a buy opportunity. Conversely, a "death cross" happens when the shorter-term MA crosses below the longer-term one, indicating a potential downtrend and a sell signal. This method provides clear, rule-based signals, which helps remove emotional decision-making from trading.
How to Implement the Moving Average Crossover
This strategy can be adapted for various timeframes, from day trading to long-term trend following. Most charting platforms include moving averages as a standard technical indicator.
- Select your moving averages: For swing trading, the 50-day and 200-day simple moving averages (SMAs) are a classic combination. For shorter-term trades, you might use exponential moving averages (EMAs) like the 12-period and 26-period EMAs.
- Confirm with volume: A crossover signal is much stronger if accompanied by high trading volume. High volume on a golden cross, for example, suggests strong buying pressure is driving the new uptrend.
- Set stop-loss orders: No strategy is foolproof. Always set a stop-loss order below your entry point on a buy signal (or above on a sell signal) to manage risk if the trend quickly reverses.
For a visual guide on setting up and interpreting these crossovers, the video below offers a detailed walkthrough.
These key steps show that the strategy's strength lies in its simplicity and clarity. By waiting for a confirmed crossover, you can filter out market noise and focus on more significant trend changes, making it an excellent starting point for new technical traders.
6. Breakout Trading Strategy
A dynamic and popular choice among beginner trading strategies, the Breakout Trading strategy focuses on capitalizing on sudden, strong price movements. The core idea is to identify key price levels, known as support and resistance, and enter a trade when the price decisively breaks through one of these barriers. The assumption is that once a significant level is breached, momentum will carry the price further in the breakout direction.
This technique is favored by traders like William O'Neil and Mark Minervini, who look for stocks emerging from established price ranges or consolidation patterns. For a new trader, this strategy offers clear entry and exit points. Instead of guessing market direction in a quiet market, you wait for a clear signal of momentum, such as a stock breaking above its 52-week high or a currency pair exiting a tight consolidation range.
How to Implement Breakout Trading
Executing this strategy requires patience and precision. The goal is to catch a new trend as it begins, which often happens when price breaks out on higher-than-average volume.
- Confirm with volume: A true breakout is typically accompanied by a spike in trading volume. Wait for this confirmation before entering a trade, as it indicates strong conviction behind the move and reduces the chance of a "fakeout."
- Set strategic stop-losses: Place your stop-loss just below the breakout level for a long position (or above it for a short position). This protects you if the breakout fails and the price reverses.
- Identify chart patterns: Practice identifying common consolidation patterns like triangles, flags, and rectangles. These patterns often precede powerful breakouts and provide a clear visual framework for planning your trade.
- Avoid low-volume periods: Breakouts are less reliable during low-volume sessions, such as midday or during holidays. Focus on periods of higher market activity, like the market open and close, for better results.
7. Mean Reversion Strategy
The Mean Reversion strategy is built on the statistical concept that asset prices and historical returns eventually revert to their long-term average or mean. This approach is one of the more analytical beginner trading strategies, assuming that extreme price moves are temporary and will correct themselves. When an asset's price deviates significantly from its historical average, traders anticipate a return to the norm, creating opportunities to buy "oversold" assets or sell "overbought" ones.
This theory is popular among quantitative traders and hedge funds who use algorithms to spot these deviations. For a new trader, it provides a logical framework for entering and exiting positions. Instead of chasing a fast-moving trend, you are essentially betting that the price has stretched too far, like a rubber band, and is due to snap back. This can be less psychologically demanding than trying to predict the direction of a breakout.
How to Implement Mean Reversion
To apply this strategy, you need tools to identify the "mean" and measure how far the current price has strayed. Moving averages and Bollinger Bands are common indicators for this purpose. For instance, a price touching the lower Bollinger Band might be considered oversold and due for a bounce.
- Identify the mean: Use a simple moving average (SMA) or exponential moving average (EMA) over a specific period (e.g., 20 or 50) to establish the average price.
- Use confirmation indicators: Don't rely on one signal. Combine indicators like the Relative Strength Index (RSI). A price far below its moving average combined with an RSI below 30 strengthens the case for a "buy" signal.
- Set clear exit points: A mean reversion trade is not a long-term hold. Your profit target should be the moving average itself. Set a tight stop-loss just beyond the recent price extreme to protect against a continued trend.
- Focus on range-bound markets: This strategy performs best when an asset is trading within a predictable range and is less effective during strong, sustained trends.
These key points highlight that success with mean reversion depends on disciplined execution and risk management. By identifying statistically likely corrections, you can find high-probability trades without needing to perfectly predict market direction.
8. Dividend Growth Investing
Another powerful method that bridges the gap between passive investing and active trading is Dividend Growth Investing. This beginner trading strategy involves buying stocks in companies that not only pay dividends but also have a long, proven history of consistently increasing those dividend payments year after year. The goal is to create a reliable and growing stream of income alongside potential capital appreciation from the stock's price.
This approach is less about short-term market timing and more about identifying financially robust companies committed to rewarding shareholders. Champions of this strategy, like David Fish who created the "Dividend Champions, Contenders, and Challengers" list, focus on the fundamental health and long-term sustainability of the business. For beginners, it provides a tangible return on investment through dividend payments, which can be a powerful motivator to stay invested during market volatility.
How to Implement Dividend Growth Investing
The key is to focus on quality companies with a track record of rewarding shareholders. Look for "Dividend Aristocrats" or "Dividend Kings," which are companies that have increased dividends for 25+ or 50+ consecutive years, respectively.
- Analyze the Payout Ratio: Ensure the company's dividend is sustainable. A payout ratio below 60% suggests the company is retaining enough earnings to fund future growth while still rewarding investors.
- Look for Consistent Growth: Target companies with at least 5-10 years of consecutive dividend increases. This demonstrates a strong commitment from management.
- Reinvest Dividends: Use a Dividend Reinvestment Plan (DRIP) to automatically buy more shares with your dividend payments. This is the engine of compounding, accelerating your portfolio's growth.
- Diversify Across Sectors: Avoid concentrating in one industry. Spread your investments across different sectors like consumer staples (e.g., Coca-Cola), healthcare (e.g., Johnson & Johnson), and utilities to reduce risk.
These key steps emphasize that the strategy’s strength lies in its dual benefit of income and growth. By selecting high-quality, dividend-paying companies and reinvesting the proceeds, beginners can build a resilient portfolio that generates passive income over time.
9. Index Fund Investing
Closely related to the Buy and Hold philosophy, Index Fund Investing is one of the most powerful and recommended beginner trading strategies for building long-term wealth. Instead of picking individual stocks, you buy a fund that mirrors a specific market index, like the S&P 500. This approach provides instant diversification across hundreds or even thousands of companies, effectively spreading your risk.
The strategy was pioneered by John Bogle, founder of Vanguard, who argued that trying to beat the market is a losing game for most investors due to fees and poor timing. By simply aiming to match market returns through a low-cost index fund, investors can capture the market's overall growth. This passive method removes the guesswork and emotional decision-making involved in active trading, making it a cornerstone for disciplined, long-term financial planning.
How to Implement Index Fund Investing
Getting started with index funds is incredibly simple, as most online brokerages offer a wide selection. Key examples include the Vanguard S&P 500 ETF (VOO) or the SPDR S&P 500 ETF Trust (SPY).
- Prioritize low expense ratios: The primary advantage of index funds is their low cost. Compare funds and choose the one with the lowest expense ratio, as this directly impacts your net returns over time.
- Consider total market funds: For even broader exposure beyond large-cap stocks, consider a total stock market index fund. This gives you a piece of small, mid, and large-cap companies.
- Stay the course: The core of index fund success is consistency. Continue investing through market highs and lows (dollar-cost averaging) and resist the temptation to sell during downturns. The goal is to capture long-term market growth, not to time short-term swings.
This strategy's brilliance lies in its simplicity and proven effectiveness. By automating your investments into a broad-market index fund and remaining patient, you harness the power of the entire economy's growth with minimal effort and cost.
10. Paper Trading Strategy
While not a direct money-making technique, the Paper Trading Strategy is arguably one of the most vital beginner trading strategies. It involves practicing with a simulated trading account funded with virtual money. This risk-free environment allows new traders to learn the mechanics of placing orders, test different strategies, and experience market movements without the fear of losing real capital. It is an indispensable educational bridge between theoretical knowledge and real-world execution.
This approach is heavily promoted by nearly all major brokerage platforms and the trading education community as a foundational step. Platforms like TradingView and TD Ameritrade's thinkorswim offer robust simulators that replicate live market conditions. By using these tools, a beginner can build confidence, refine their approach, and make initial mistakes on paper instead of with their hard-earned money.
How to Implement Paper Trading
Getting started is as simple as opening a demo account with a reputable broker. The goal is to create a realistic trading environment to prepare you for live markets.
- Treat simulated money as real: To get the most out of the experience, handle your virtual capital with the same discipline and emotional consideration you would with real funds.
- Keep a detailed trading journal: Document every trade, including your entry and exit points, the reason for the trade, and the outcome. This journal is crucial for identifying patterns in your decision-making.
- Practice strict risk management: Apply rules like the 1% rule, where you never risk more than 1% of your virtual account on a single trade. This builds essential habits for capital preservation.
- Test a strategy for several months: Before going live, test your chosen strategy consistently for at least three months to ensure it performs well across different market conditions.
Beginner Trading Strategies Comparison Matrix
| Strategy | Implementation Complexity 🔄 | Resource Requirements ⚡ | Expected Outcomes 📊 | Ideal Use Cases 💡 | Key Advantages ⭐ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Buy and Hold Strategy | Low – minimal trading | Low – initial capital | Steady long-term growth, compound returns | Long-term investors, beginners | Low costs, low stress, tax benefits |
| Dollar-Cost Averaging (DCA) | Low – fixed regular investments | Low – small periodic deposits | Reduced volatility impact, average cost lowering | Investors facing volatile markets | Disciplined approach, eliminates market timing |
| Trend Following Strategy | Moderate – requires technical analysis | Moderate – chart tools | Profit from strong trends, momentum gains | Trending markets, active traders | Objective rules, captures big moves |
| Support and Resistance Trading | Moderate – skill to identify levels | Moderate – charting tools | Defined entry/exit points, good risk-reward | All markets, all timeframes | Clear signals, easy to combine with others |
| Moving Average Crossover | Moderate – requires indicator setup | Moderate – technical platforms | Trend confirmation, clear buy/sell signals | Trending markets, automated trading | Simple, removes emotion, easily automated |
| Breakout Trading Strategy | High – quick decisions & volume confirmation | High – monitoring & execution | Capture large moves post-breakout | Volatile markets, active traders | Objective entries, strong risk-reward |
| Mean Reversion Strategy | Moderate – statistical analysis | Moderate – indicator setup | Consistent small profits in range-bound | Sideways/low volatility markets | Predictable risk, works in sideways conditions |
| Dividend Growth Investing | Low – fundamental analysis | Moderate – capital for dividends | Income & capital growth over long term | Income-focused, long-term holding | Regular income, inflation protection |
| Index Fund Investing | Low – passive buy and hold | Low – minimal fees & capital | Market-average returns, broad diversification | Beginners, passive investors | Instant diversification, very low fees |
| Paper Trading Strategy | Low – simulated environment | Low – platform access | Learning, strategy testing without risk | All beginner traders | No financial risk, build confidence |
Putting Your Knowledge into Action
You have now journeyed through ten distinct beginner trading strategies, from the long-term patience of Buy and Hold to the active, chart-driven approach of Breakout Trading. This diverse toolkit provides a solid foundation, but the most crucial step is translating this knowledge into consistent, disciplined action. The path to profitable trading isn't about finding a single "holy grail" strategy; it's about finding the strategy that fits you.
The real work begins now. Your primary goal is to bridge the gap between theory and real-world application. Information alone doesn't generate returns; disciplined execution does. The strategies we've discussed, such as Support and Resistance Trading or the Moving Average Crossover, are not just abstract concepts. They are frameworks for making objective decisions in an often-emotional environment.
Your Actionable Path Forward
To truly master these concepts and build lasting confidence, you must commit to a structured process of practice and refinement. Avoid the common pitfall of "strategy hopping," where a trader jumps to a new method after a few losses. True proficiency is built through repetition and deep understanding.
Here are your immediate next steps:
- Select Your Focus: Choose one or two strategies from this list that resonate most with your personality and schedule. Are you a patient, long-term investor suited for Dollar-Cost Averaging, or do you prefer the active engagement required for Trend Following?
- Embrace Paper Trading: Open a demo account and begin applying your chosen strategies without risking real capital. The Paper Trading strategy we covered isn't just an item on a list; it is your essential training ground. Use it to test your setups, practice entries and exits, and learn to manage your emotions.
- Develop a Trading Plan: For your chosen strategy, define your rules. What specific criteria will signal a buy or sell? What is your maximum risk per trade? How will you take profits? A written plan removes guesswork and enforces discipline.
- Master Risk Management: This is the non-negotiable bedrock of trading. No strategy can succeed without it. Always know your potential loss before entering a trade and never risk more than you are truly willing to lose.
The ultimate value of learning these beginner trading strategies lies in building a robust framework for interpreting market behavior. Whether you are analyzing support levels or identifying a new trend, you are learning to read the language of price action. This skill is transferable across all markets and timeframes, serving as the core of your trading education. By starting with these foundational methods, you are not just learning to follow rules; you are learning to think like a trader, preparing you to adapt and thrive as market conditions change.
Ready to move beyond basic concepts and master the art of price action? The professional trading course from Colibri Trader provides the in-depth education and practical mentorship needed to build a sustainable trading career. Learn the exact strategies used by professional traders by visiting Colibri Trader today.