What is Leverage in Forex? Explained & Key Insights
When you first step into the world of forex trading, you’ll hear the word leverage thrown around a lot. So, what is it?
Think of it as a tool your broker gives you. It’s essentially a loan that lets you control a much larger position in the market with just a small amount of your own money. This is what gives you more trading power, but it’s a double-edged sword—it magnifies your potential profits and your potential losses in equal measure.
Your First Look at Forex Leverage
The easiest way to understand leverage is to picture it as a financial magnifying glass. It takes a small slice of your own capital—what we call margin—and dramatically expands its impact.
It’s a lot like putting a 5% down payment on a house. You don’t own the whole property outright, but you control it. In the same way, a small margin deposit allows you to control a much larger currency trade. This is the mechanism that allows traders with more modest accounts to participate in the forex market.
Of course, with great power comes great responsibility. The idea of bigger profits is exciting, but the risk of bigger losses grows right alongside it. Getting your head around this dual nature is the single most important first step for any new trader.
The core idea is simple: You are using borrowed capital to increase the potential return of an investment. In forex, this means your broker fronts the majority of the trade value, while you provide a smaller, good-faith deposit.
Breaking Down the Key Terms
To really get a feel for how leverage works, you need to know a few other key terms. They all fit together and are the building blocks of every single leveraged trade.
If you want to go deeper on these fundamentals, our guide on forex basics like margin, leverage, and lot size breaks it all down in more detail.
For now, let's get you started with a quick reference.
Key Leverage Concepts at a Glance
This simple table breaks down the core components of forex leverage. It’s a great way for new traders to get a clear and quick reference on the key ideas.
| Concept | Simple Explanation | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Leverage Ratio | This shows how much larger your trade is compared to your own capital (margin). A 100:1 ratio means for every $1 of your money, you can control $100 in the market. | Your broker offers 50:1 leverage. |
| Margin | This is the amount of your own money you need to put up to open and hold a leveraged position. It's not a fee—think of it as a security deposit your broker holds. | To open a $50,000 position with 50:1 leverage, you need to put up a margin of $1,000 (1/50th of the position size). |
Understanding these two concepts—the ratio offered and the deposit required—is the foundation of using leverage responsibly.
How Leverage Works in a Real Forex Trade

Okay, let's move past the textbook definitions and see how this actually plays out in a real trade. This is where the concept of leverage really clicks for most traders.
Picture this: you've got $1,000 in your trading account. You’ve been watching the EUR/USD, and you have a strong feeling the Euro is about to climb against the US Dollar.
You want to get in on that move, but with only $1,000, your potential profit feels pretty limited. This exact moment is why leverage exists. Your broker steps in and offers you 100:1 leverage, essentially handing you a tool to amplify your trading power.
What does 100:1 actually mean? It’s a ratio. For every $1 of your own money you put up, the broker lets you control $100 in the market. It’s a game-changer.
Putting Your Capital to Work
That 100:1 ratio transforms your modest $1,000 account. Suddenly, you have the ability to command a $100,000 position.
Here’s the simple math behind it:
- Your Capital: $1,000
- Leverage Ratio: 100:1
- Total Position Size: $1,000 (Your Capital) x 100 (Leverage) = $100,000
You’ve just opened a $100,000 trade on EUR/USD, but you only used $1,000 of your own cash to do it. The other $99,000 is a short-term loan from your broker, giving you that massive market exposure.
Now, that $1,000 from your account isn’t a fee that disappears. It's held as something called margin.
Think of margin as a good-faith deposit. Your broker sets aside this portion of your funds to open the leveraged trade and cover any potential initial losses, ensuring you have "skin in the game."
The Role of Margin in a Leveraged Trade
The amount of margin you need is tied directly to your leverage. The more leverage you use, the less margin you need to post for the same-sized trade.
With a 100:1 leverage ratio, the margin requirement is 1% of the total position value.
Let's plug in the numbers from our trade:
- Total Trade Value: $100,000
- Margin Requirement (1%): 0.01 x $100,000 = $1,000
That $1,000 is now "locked up" to keep your position open. Since you started with $1,000, your "free margin"—the cash available to open other trades—is currently $0. This is the core engine of a leveraged trade: your small deposit now controls a significant stake in the market.
The Power and Peril of Using Leverage

It’s one thing to know the textbook definition of leverage, but it’s another thing entirely to respect its dual nature. This is what separates traders who stick around from those who quickly burn through their accounts.
Leverage is an incredible tool. It’s a double-edged sword that magnifies opportunity, but you have to remember it cuts both ways with equal force. Success requires a balanced view, appreciating its power to create profits just as much as its capacity for gut-wrenching losses.
On one hand, leverage is the great equalizer in the forex market. It’s what allows traders with smaller accounts to command meaningful positions, turning tiny market ripples into substantial gains. Without it, a trader with $1,000 would see pocket change from the small, fractional price moves typical of currency pairs.
The Clear Upside of High Leverage
The main advantage is simple: you get amplified buying power. This brings a few key benefits to the table for the everyday retail trader.
- Massive Profit Potential: A small price move in your favor can translate into a huge percentage return on the money you actually put up (your margin).
- Smarter Capital Use: You can control a large position without tying up all your trading capital. This frees up your funds for other trades you might spot.
- Market Access for Everyone: You don’t need tens of thousands of dollars to get in the game. Leverage lets people with more modest account sizes participate in a real way.
In the past, forex leverage ratios were much higher than in other markets. It wasn’t uncommon for retail traders to get access to 100:1 or even 500:1 leverage. But regulators in key markets like the US, EU, and Australia have stepped in, recognizing the immense risks. For example, the US Commodity Futures Trading Commission (CFTC) capped retail forex leverage at 50:1 for major pairs all the way back in 2010 to protect traders. You can explore more forex trading statistics to see just how much the landscape has shifted.
The Unforgiving Risks You Absolutely Cannot Ignore
For every story of a massive win fueled by leverage, there’s a cautionary tale of a wiped-out account.
The very same force that blows up your gains will amplify your losses just as brutally—and often much faster than you’d ever expect. A tiny market move against your position can eat through your margin with frightening speed.
This brings us to one of the most dreaded events in a trader's journey: the margin call.
A margin call is not a friendly phone call from your broker. It's an automated alert telling you that your account has dropped below the required level to keep your trades open. If you don't add more money—fast—your broker will start closing your positions automatically to stop the bleeding. This locks in your loss.
It’s a safety net designed to stop your account from going negative, but it’s a harsh lesson in risk management.
The key takeaway is this: leverage doesn't just increase your potential reward; it dramatically raises the stakes of every single trade. Ignoring that reality is the fastest way to get kicked out of the market.
Leverage in Action: A Tale of Two Trades
Let's get practical. To really understand the double-edged sword that is forex leverage, abstract ideas just don't cut it. The best way to see the impact is to walk through two opposing, real-world trading scenarios. You'll see how the exact same small market move can lead to drastically different results.
The Winning Trade: A Story of Amplified Success
Picture this: you have $1,000 in your trading account. You decide to go long on the GBP/USD pair, betting that the British Pound is about to climb. By using 100:1 leverage, your $1,000 margin now commands a $100,000 position in the market.
Turns out, your analysis was spot on. The GBP/USD exchange rate ticks up by just 1%.
Now, without leverage, a 1% gain on your $1,000 would have netted you a measly $10. But with that leveraged position, the game completely changes. A 1% gain on $100,000 is $1,000.
You close the trade. Just like that, you've doubled your initial capital, locking in a 100% return from a tiny market shift. This is the incredible power of leverage in action.
The Losing Trade: A Cautionary Tale
Okay, let's hit rewind and play that same trade again, but this time, the market turns against you. You open the same $100,000 GBP/USD position with your $1,000 margin.
This time, though, the market moves against you by 1%. That 1% loss isn't based on your $1,000 margin; it's calculated on the full $100,000 position. The loss is $1,000.
Since your margin was $1,000, that single move just wiped out your entire investment for this trade. Your broker would issue a margin call and liquidate the position, cementing a 100% loss. This is the brutal flip side of leverage—where a small dip can have devastating consequences.
To truly hammer this home, let's compare these two outcomes side-by-side.
Leverage Scenario Comparison: Profit vs. Loss
| Metric | Winning Trade Scenario | Losing Trade Scenario |
|---|---|---|
| Initial Capital | $1,000 | $1,000 |
| Leverage Ratio | 100:1 | 100:1 |
| Position Size | $100,000 | $100,000 |
| Market Movement | +1% (Favourable) | -1% (Adverse) |
| Profit / Loss | +$1,000 | -$1,000 |
| Account Impact | +100% Gain | -100% Loss |
As you can see, leverage is a pure amplifier. It takes whatever outcome you get—good or bad—and magnifies it.
This visual shows the direct relationship between different leverage ratios and the margin you need to put up.
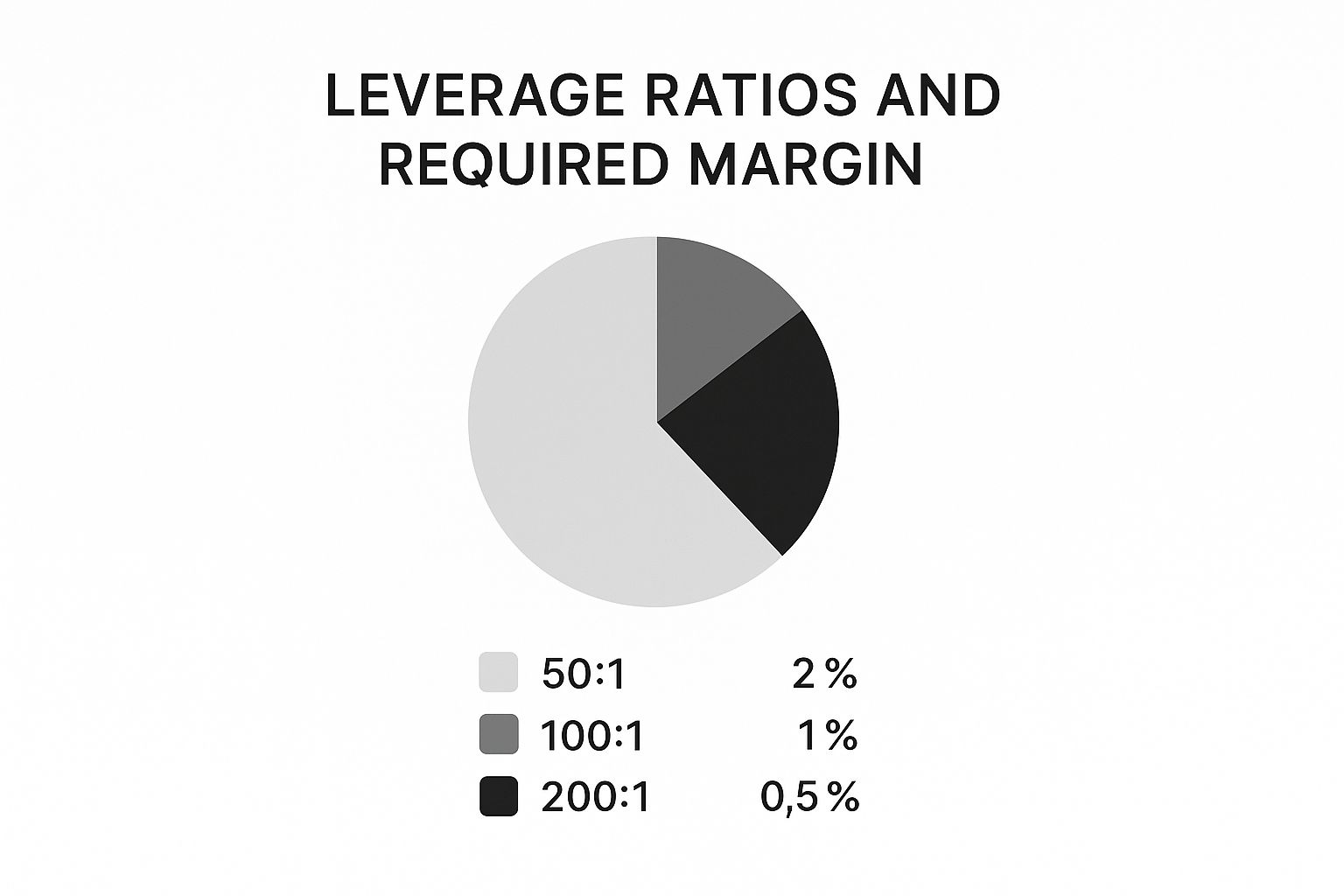
As the infographic shows, higher leverage means you need to commit less of your own capital upfront as margin, which is precisely why it's so tempting for new traders.
History offers a stark reminder of these risks. One of the most dramatic examples was the Swiss Franc shock on January 15, 2015. The Swiss National Bank unexpectedly abandoned its currency peg, causing the Franc to rocket up by 20% almost instantly. This "black swan" event triggered catastrophic losses for countless highly leveraged traders and even bankrupted several brokers whose clients lost far more than they had in their accounts. You can learn more about how major forex events shaped trading history to see just how powerful these market shifts can be.
Choosing the Right Leverage for Your Strategy

So, you've got the basics of forex leverage down. The next, and most critical, step is learning how to use it without blowing up your account.
It’s a classic rookie mistake: see a broker offering massive 500:1 leverage and immediately jump on it, dreaming of huge profits. Let me tell you from experience, that's a one-way ticket to disaster.
The pros treat leverage as a strategic tool, not a default setting. The right amount isn't some magic number; it's a careful decision that aligns with your trading plan and how much risk you can stomach.
Factors That Should Guide Your Leverage Choice
Before you even think about picking a leverage ratio, you need to take a hard look at a few key variables. Each one directly impacts how much heat you're taking on with every single trade.
- Your Risk Tolerance: Are you the kind of trader who obsesses over protecting your capital? Or are you comfortable with bigger swings for a shot at bigger returns? Be honest with yourself. This is your first line of defense.
- Currency Pair Volatility: Trading a relatively stable pair like EUR/USD is a different ballgame than trading a volatile emerging market currency. The wilder the pair, the less leverage you should use to avoid getting stopped out by a sudden spike.
- Your Trading Strategy: A scalper trying to grab a few pips here and there might use higher leverage on tiny positions. A long-term position trader, on the other hand, will use much, much lower leverage to ride out market waves over weeks or even months.
The goal is to make your leverage fit your strategy, not force your strategy to fit the leverage. It should be a tool that serves your goals and protects your account, turning a pure gamble into a calculated risk.
Comparing Leverage Levels: A Practical Look
Let's break down how different leverage ratios can completely change the game on a $1,000 account.
With 10:1 leverage, you can control a $10,000 position. If the market moves against you by 1%, that's a $100 loss, or 10% of your account. It stings, but you live to trade another day.
Now, let's crank it up to 100:1. This lets you control a whopping $100,000 position. That exact same 1% adverse move now translates to a $1,000 loss. Your entire account is wiped out. Gone. On a single trade.
This simple math shows why lower leverage is almost always the smarter path, especially when you're starting out. Choosing the right ratio is a cornerstone of your success, and it’s why it's so vital to understand https://www.colibritrader.com/how-to-make-a-trading-plan/ before you put real money on the line.
The foreign exchange market is a beast, with an average daily turnover hitting $6.6 trillion. While the big players like hedge funds might use high leverage, the retail traders who survive and thrive are the ones who understand that keeping your capital safe is job number one.
Smart Risk Management for Leveraged Trading
Getting your head around what leverage is in forex is only half the battle. Knowing how to control it is what separates the traders who stick around from those with blown accounts.
Success in leveraged trading isn't about chasing lottery-ticket profits. It’s about being smart enough to survive the losses that are an inevitable part of the game. This means you need a disciplined, non-negotiable approach to managing your risk on every single trade you take.
Think of these techniques as your essential safety gear. Without them, you're flying blind in a very fast-moving market. The most crucial tool in your kit is the Stop-Loss order. This is a direct instruction to your broker to automatically get you out of a trade if it hits a price level you've decided on beforehand.
Setting a Stop-Loss isn't a suggestion; it's your financial seatbelt. It defines your maximum acceptable loss before you even click the buy or sell button, making sure one bad idea doesn't wipe you out.
The Trader's Essential Toolkit
A Stop-Loss is your first line of defense, but you need more in your arsenal to really protect your capital. These tools all work together to build a solid defensive wall around your trading account. For a much deeper look into how the pros do it, checking out this guide on managing trading risk will give you some powerful insights.
Here are the other core pieces every trader must master:
-
Take-Profit Orders: A Stop-Loss protects your downside, and a Take-Profit order does the opposite—it locks in your winnings. It’s an order that automatically closes your trade when it hits your profit target. This stops you from letting greed turn a great trade into a terrible one.
-
The 1% Rule: This is the bedrock of professional trading. The rule is simple: never risk more than 1% of your total account balance on a single trade. If you're trading with a $5,000 account, your maximum loss on any one position should be no more than $50. Period.
-
Position Sizing: This ties everything together. Based on your Stop-Loss distance and the 1% rule, you calculate exactly how large your position should be. This keeps your risk consistent trade after trade and stops you from accidentally putting on a position so big it could cripple your account.
When you start combining these three elements—Stop-Loss, Take-Profit, and disciplined position sizing—you move away from gambling and into the world of calculated risk-taking. This is the strategic framework that lets you use leverage as the powerful tool it can be, all while keeping your capital safe for the long haul.
Common Questions About Forex Leverage
Once you start wrapping your head around the idea of leverage, the practical questions really start to bubble up. It's totally normal. Let’s walk through a few of the most common ones I hear from traders to iron out any confusion.
What Is a Good Leverage Ratio for a Beginner?
This is probably the single most important question a new trader can ask. You’ll see brokers dangling massive leverage ratios like 100:1 or even 500:1, and it’s tempting. But honestly? Stay away from that, at least for now.
For someone just starting out, a 10:1 or 20:1 ratio is a much smarter, safer place to be.
This more conservative approach lets you learn the ropes of trading with leverage without the terrifying risk of blowing up your account on one bad trade. Lower leverage forces you to be more disciplined and gives you the breathing room to make mistakes—and you will make mistakes—while you find your footing.
Key Takeaway: Ignore the temptation of sky-high leverage when you're new. Your first job is not to get rich quick; it's to protect your capital while you learn the craft. Starting small isn't just for beginners; it's what the pros do.
Can I Trade Forex Without Any Leverage?
Yep, you absolutely can. Trading without any leverage is called trading on a 1:1 basis. It means every single dollar in your trading position is backed by a dollar from your own account.
The catch? The forex market moves in incredibly small increments known as pips.
Without leverage, you'd need a massive amount of capital just to see any kind of meaningful profit from these tiny price fluctuations. For most retail traders, that just isn't practical. Leverage is really the tool that makes it possible for traders with smaller accounts to generate significant returns.
How Do I Calculate Potential Profit or Loss?
Knowing how to figure out your potential profit or loss is absolutely critical for managing your risk. The main thing to remember is this: your profit or loss is always calculated on the total size of your leveraged position, not just the small bit of margin you put up.
Let's break it down. Say you open a $50,000 position. If the market moves 1% in your favor, you've made $500. If it moves 1% against you, you've lost $500.
Now, if you used 50:1 leverage to open that position, your actual margin was only $1,000. That means a simple 1% move in the market translated to a massive 50% gain or loss on the capital you actually put on the line for that trade. It’s a double-edged sword, and you have to respect it.
At Colibri Trader, we teach you how to master price action and manage risk effectively, turning trading into a skill, not a gamble. Discover your trading potential by visiting us at https://www.colibritrader.com.