How to Start Forex Trade A Realistic Guide for Beginners
If you're looking to get started in forex trading, the path is pretty straightforward on the surface: you'll need to open an account with a regulated broker, put some capital in it, and then learn the ropes of analysing how currency prices move. But the real key to success isn't just about the mechanics; it's about building a solid strategy and managing your risk like a hawk. It's definitely not about chasing those get-rich-quick fantasies you see online.
Understanding the Forex Market Without the Hype

Before you even think about placing your first trade, it's crucial to cut through all the marketing noise. The foreign exchange (forex or FX) market is often painted as an easy path to wealth, but that's a far cry from reality. Getting a grip on the fundamentals is the first real step toward building a sustainable trading career.
At its core, forex trading is simply exchanging one currency for another. When you trade a pair like EUR/USD, you're really just speculating on where the Euro's value is headed in relation to the U.S. Dollar. If you think the Euro is going to get stronger, you buy the pair. If you predict it's going to weaken, you sell. Simple as that.
The Double-Edged Sword of Liquidity
One of the first things you'll hear about the forex market is its massive size and liquidity. When you start trading forex, you're stepping into an arena where the average daily trading volume is around $7.51 trillion as of early 2025. This incredible scale—driven by huge institutions, governments, and retail traders like us—means you can almost always get in or out of a trade instantly.
But that high liquidity can be a double-edged sword, especially when you're new. While it makes for smooth trades, it also means prices can whip around violently, particularly when big economic news hits. That volatility can wipe out an account just as fast as it can create an opportunity.
The forex market doesn't reward haste or luck. Your success will be directly proportional to the effort you put into education, strategy development, and, most importantly, discipline. Rushing in without a plan is the fastest way to deplete your capital.
Setting Realistic Expectations
For any new trader, the number one goal should be preserving your capital, not making a fortune overnight. The journey really begins with understanding how the market actually works. This is a field where knowledge, a clear plan, and disciplined execution are your greatest assets.
Forget the hype. Real trading is about:
- Consistent Learning: The market is always evolving. Your education never stops.
- Strategic Planning: Every single trade needs to be part of a well-defined strategy with clear entry and exit points.
- Emotional Control: Managing fear and greed is, without a doubt, the hardest part of trading.
- Risk Management: Protecting your account from a catastrophic loss isn't just important—it's everything.
To give you a clearer picture of the milestones ahead, here’s a quick checklist that outlines the essential steps for any new trader.
Forex Trading Quick Start Checklist
| Milestone | Action Required | Key Focus |
|---|---|---|
| Education Foundation | Complete a beginner forex course or read foundational books. | Understanding core concepts like pips, lots, and leverage. |
| Broker Selection | Research and open an account with a regulated broker. | Regulation, spreads, fees, and platform reliability. |
| Platform Mastery | Learn the trading platform inside and out on a demo account. | Placing orders, setting stop-loss, using indicators. |
| Strategy Development | Choose a simple strategy (e.g., support/resistance). | Defining clear entry, exit, and risk rules. |
| Risk Management Plan | Define your risk-per-trade (e.g., 1-2% of account). | Capital preservation and emotional control. |
| First Live Trades | Start with the smallest possible trade size. | Following your plan, not the P/L. |
This foundation is crucial before you risk a single dollar of real money. By approaching the market with respect and a genuine commitment to learning, you set yourself up for long-term participation instead of a short, expensive lesson.
If you're ready to dig deeper into the mechanics, our detailed guide on how forex trading works is a great next step.
Choosing Your Broker and Trading Platform
Picking the right broker is easily one of the most critical decisions you'll make when you start trading forex. This goes way beyond just finding a company with a slick website. Your broker is your direct gateway to the markets, and everything from their reliability to their platform can make or break your trading experience—not to mention the safety of your money.
Think of it like choosing a business partner. A little due diligence now can save you from massive headaches down the road.
The explosion in retail trading has flooded the market with options. The global forex broker market was valued at an eye-watering $5.2 trillion in 2023 and is projected to hit $13 trillion by 2032. With that much cash flying around, you've got to be careful to separate the reputable players from the sketchy ones.
Don't Skip the Regulatory Check
Before you even look at spreads or platforms, the absolute first thing you need to verify is regulation. A broker’s regulatory status is your primary line of defense. Reputable financial authorities force brokers to follow strict rules, like keeping your funds in segregated accounts, completely separate from their own operational cash.
You want to see oversight from top-tier regulators like:
- Financial Conduct Authority (FCA) in the United Kingdom
- Cyprus Securities and Exchange Commission (CySEC) in Cyprus
- Australian Securities and Investments Commission (ASIC) in Australia
If a broker isn't regulated by a major authority, that's a huge red flag. Unregulated brokers are the wild west of finance, and you’re putting your capital at serious risk by dealing with them.
Choosing a well-regulated broker isn't just a suggestion; it's a non-negotiable. The peace of mind that comes from knowing your funds are protected is invaluable.
Understanding the True Costs of Trading
Brokers make their money in a couple of main ways: spreads and commissions. The spread is that tiny difference between the buy (ask) and sell (bid) price of a currency pair. The tighter the spread, the less it costs you to get in and out of a trade.
On top of that, some brokers charge a commission, which is a flat fee for each trade. You might find a broker offering zero-spread accounts but charging a commission, or the other way around. You have to look at the total cost—spreads plus commissions—to really figure out which broker is the most cost-effective for the way you plan to trade.
Selecting Your Trading Platform
The trading platform is your command center. It's the software you’ll be staring at for hours, analyzing charts, placing orders, and managing your positions. For both beginners and pros, the undisputed kings of the platform world are MetaTrader 4 (MT4) and MetaTrader 5 (MT5).
Here’s a glimpse of the MetaTrader 5 interface, which is a popular choice for its advanced charting tools and clean, user-friendly design.

As you can see, it gives you everything you need—charting windows, market watchlists, and your account info—all in one place.
Almost every good broker offers a free demo account, which is the perfect way to test-drive their platform. Use it! See how it feels. Is it intuitive or clunky? Are the charts easy to work with? How fast are orders executed? Your platform should feel like an extension of your own analysis, not something you have to fight with.
For a deeper look, check out our guide on the best trading platforms for beginners to see how the top options stack up against each other.
Learning to Read the Market

Alright, so how do you actually decide when to click "buy" or "sell"? It all comes down to your analysis—your personal method for figuring out where a currency pair is most likely headed. I know this can feel like the most intimidating part when you're just starting, but it really boils down to two core approaches.
You don’t have to master both right away. In my experience, most traders eventually find a style that clicks for them, gravitating toward one while still keeping an eye on the other. Let's pull back the curtain on these two schools of thought.
The Story Behind the Price: Fundamental Analysis
Fundamental analysis is all about the "why." It's the practice of connecting real-world economic news, social shifts, and political events to the value of a currency. When a central bank hikes interest rates, for example, that country's currency often gets stronger because it offers a better return to investors. Simple as that.
Think of a country's currency as a share of stock in its economy. Good news usually boosts its value, while bad news can send it tumbling.
Traders who lean on fundamentals are always watching:
- Major Economic Reports: Data releases on things like Gross Domestic Product (GDP), inflation (CPI), and employment numbers (like the U.S. Non-Farm Payrolls) are massive market movers.
- Central Bank Announcements: Pay attention when institutions like the Federal Reserve or the European Central Bank talk about interest rates. Their statements can trigger instant, high-impact price swings.
- Geopolitical Events: Elections, new trade deals, and international conflicts all add layers of risk and uncertainty that ripple directly through currency markets.
A real-world example? A fundamental trader might decide to sell the Japanese Yen (JPY) after hearing the Bank of Japan plans to keep interest rates near zero while other major economies are raising theirs. The logic is that money will flow out of the JPY and into higher-yielding currencies.
Don't feel like you need to become an economist overnight. A great first step is to simply pull up an economic calendar and watch how the market reacts to major news for one or two currency pairs. This kind of observation is your best teacher.
The Art of Chart Reading: Technical Analysis
While fundamentals explain why a market might be on the move, technical analysis is purely focused on how it's moving. This is the art of reading price charts to spot patterns, trends, and likely turning points based entirely on historical price action. The core belief here is that all the news and data are already baked into the price you see on the screen.
Technical analysts use charts as a roadmap, searching for clues about where the price might go next. This involves hunting for key price levels and patterns that have mattered in the past.
One of the most powerful—and basic—concepts here is support and resistance.
- Support: This is a price level where a downtrend tends to stall out because of a concentration of buyers. Think of it as a floor the price has a hard time breaking through.
- Resistance: The polar opposite of support. It's a price level where an uptrend is likely to hit a wall or even reverse, acting as a ceiling.
If you look at any chart, you'll see the price never moves in a perfectly straight line. It bounces between these "floor" and "ceiling" levels. Learning to spot them gives you a simple, visual framework for deciding where a good entry point might be and—just as critically—where your trade idea might be proven wrong.
Building Your Risk Management Playbook
Alright, let's talk about the single most important topic in trading. This is the part that separates the pros who last for decades from the hobbyists who blow up their accounts in a few months.
Winning trades feel fantastic, don't get me wrong. But your long-term success isn’t defined by your winners. It’s defined by how you handle your losses. This is where you build the discipline to stay in the game long enough to actually get good at it.
Your number one tool for protecting your capital is the stop-loss order. This is a non-negotiable instruction you give your broker to automatically close a losing trade once it hits a certain price. Think of it as your emergency brake; it caps your maximum loss on any single trade, preventing a bad decision from turning into a catastrophic one.
Trading without a stop-loss is like driving a race car without brakes. You're just asking for a disaster.
The 1% Rule: Your Career Lifeline
So, how do you decide where to place that stop-loss? It all starts with a simple, powerful rule that has saved more trading careers than any complex strategy ever will.
The most respected rule of thumb in this business is to never risk more than 1% of your trading account on a single trade. Some will stretch this to 2%, but for a beginner, 1% is the gold standard. This is the bedrock of capital preservation.
Let’s say you’re working with a $2,000 account. A 1% risk means the absolute most you can lose on one trade is $20. That’s it. This simple constraint forces you to calculate your trade size based on your stop-loss distance, not the other way around. It ensures that even a brutal string of five or ten consecutive losses won’t knock you out of the game.
Losing is just a part of trading. The goal isn't to avoid losses—it's to make sure they're small and completely manageable. The 1% rule is your single best defense against emotional decisions and the kind of major drawdowns that end trading careers before they even begin.
This approach keeps you focused on the process, not just the profit. The forex market is vast and full of opportunity, with more than 170 different currencies traded daily. As global trade expands, so does the need for currency exchange, and modern platforms have made it easier than ever for new traders to get involved. You can get a sense of just how massive this market is by checking out some fascinating forex statistics from The Tokenist.
To really drive this home, let’s look at how the 1% rule plays out in different scenarios.
Risk Scenarios Using the 1% Rule on a $1,000 Account
The table below breaks down exactly how the 1% rule ($10 max risk) works with different trade sizes. Notice how a larger trade size forces you to use a much tighter stop-loss to keep your risk constant.
| Currency Pair | Trade Size (Lots) | Max Dollar Risk | Stop-Loss Distance (Pips) |
|---|---|---|---|
| EUR/USD | 0.01 (Micro) | $10 | 100 pips |
| EUR/USD | 0.02 (Micro) | $10 | 50 pips |
| EUR/USD | 0.05 (Micro) | $10 | 20 pips |
| EUR/USD | 0.10 (Mini) | $10 | 10 pips |
This shows you that your trade idea (where you place your stop) directly dictates how large of a position you can take. It’s a mathematical process, not a gut feeling.
Putting It All Together in a Real Trade
Let's walk through a real-world scenario to see how these concepts click into place.
Imagine you have a $1,000 account and you're looking to buy the EUR/USD.
-
Define Your Risk: First thing's first. You’re sticking to the 1% rule, so your maximum acceptable loss on this trade is $10. No exceptions.
-
Identify Your Invalidation Point: You've looked at the chart and decided your trade idea is proven wrong if the price drops 20 pips. This is where you'll set your stop-loss. It's your "I'm wrong" line in the sand.
-
Calculate Position Size: Now for the final piece. You need to calculate a position size where a 20-pip move against you equals exactly your $10 risk limit. (Hint: Looking at the table above, that would be a 0.05 lot size).
This systematic process completely removes guesswork and emotion. Your trading decisions become mathematical and strategic, not impulsive reactions to a wiggling chart. Building this playbook is the most important step you will ever take in your trading journey. It’s what turns this from a gamble into a business.
Executing Your First Trade in a Demo Account
Knowing the theory is one thing, but actually clicking the buttons on a trading platform when the market is moving is a completely different ball game. This is precisely why a demo account is your single most important tool starting out. It lets you apply everything you've learned in a live market environment, but without risking a single dollar.
Think of it as your personal trading sandbox.
The goal here isn't to rack up imaginary millions. It’s about building mechanical skill and emotional discipline. You want the entire process—analyzing a chart, figuring out your risk, and placing the order—to become second nature. This risk-free practice is what prepares you for the real deal, long before you even think about funding a live account.
Finding a High-Probability Setup
Let's walk through a real-world scenario. Imagine you're looking at the GBP/USD chart. You notice that the price has bounced off a very clear support level around 1.2500 multiple times. Your analysis tells you that if the price pulls back to this level one more time, there's a good chance it will rally again.
This is your trade idea—a potential long (buy) entry.
So, you form a clear plan:
- Entry Point: You'll buy if the price touches the 1.2500 support level.
- Invalidation Point (Stop-Loss): If the price drops to 1.2470, your idea is wrong. You need to get out to prevent bigger losses. That’s a 30-pip stop-loss.
- Profit Target: You spot a previous resistance area up around 1.2590. That seems like a logical place to take your profit, giving you a 90-pip potential reward.
The most critical part of this entire process is defining your exit points before you ever get into the trade. Your stop-loss is there to protect your capital, and your take-profit locks in your gains. Never, ever enter a trade without knowing exactly where you'll get out for both a win and a loss.
This whole process of practicing in a demo account has a name: paper trading. It's a non-negotiable step that even seasoned pros use to test out new strategies. To get a better handle on its benefits, you can check out this detailed guide on what paper trading is and why it’s so vital.
Calculating Your Position and Placing the Order
Now, let's pull in the risk management rules we talked about. Let's say you have a $5,000 demo account. Following the 1% rule, the absolute most you can risk on this single trade is $50.
Your stop-loss is 30 pips. Now you need to calculate a position size that makes those 30 pips equal your $50 risk limit. Using a position size calculator (a standard tool on almost any platform), you figure out the correct size is about 0.17 lots.
With all the prep work done, you're ready to place the order. On your trading platform, you'd do the following:
- Select GBP/USD.
- Click "New Order."
- Enter the volume (or lot size): 0.17.
- Set your Stop-Loss price at 1.2470.
- Set your Take-Profit price at 1.2590.
- Place a "Buy Limit" order at your planned entry price of 1.2500.
This visual guide breaks down the core logic of position sizing, setting stops, and evaluating the risk-to-reward ratio for every trade.
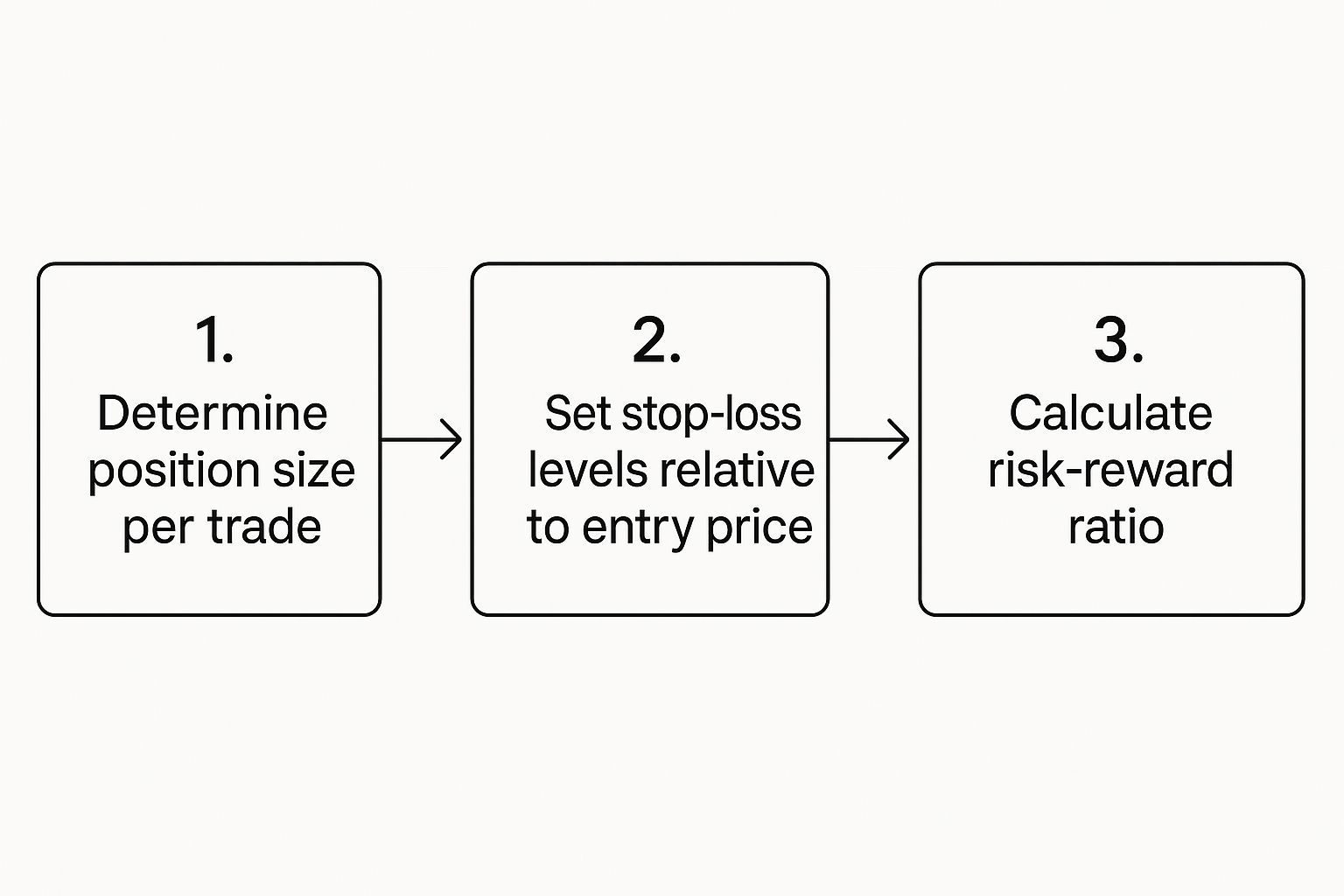
This graphic drives home a key point: your risk management rules—not a gut feeling—should always dictate your trade parameters.
With a 30-pip risk for a 90-pip reward, your risk-to-reward ratio is a fantastic 1:3. This means your potential profit is three times larger than your potential loss, which is the hallmark of a quality trade setup. Keep repeating this process in your demo account until it becomes automatic.
When you're just starting out in forex, a million questions probably run through your head. It's totally normal. Getting some straight, honest answers can make those first steps feel a lot less intimidating. Let's clear up a few of the most common things new traders ask me.
How Much Money Do I Need to Start Forex Trading?
You'll see brokers everywhere advertising that you can open an account with just $10. While that's technically true, it's not practical. In my experience, a realistic starting point is at least $500.
Here's why: with a tiny account balance, you can't manage your risk properly. It's that simple. Even the smallest possible trade size, a micro lot, would be a huge chunk of your account. This completely blows up the essential 1-2% risk rule that keeps traders in the game. Starting with $500 or more actually gives you the breathing room to apply this rule, so a single trade doesn't threaten your entire account.
Should I Start with a Demo or a Live Account?
There is only one answer to this, and it’s non-negotiable: always begin with a demo account.
Think of it as a flight simulator for traders. It’s a completely risk-free playground where you can get the hang of your trading platform, see how your strategies perform in real-time market conditions, and practice executing trades until it's second nature.
Treat your demo trading like it's real money. The whole point is to build the right habits and discipline before your capital is on the line. I always tell my students to trade on a demo for at least a month, or until they have a solid track record of consistent results that follow their trading plan.
This practice is where you iron out all the kinks. Rushing this stage is one of the most expensive mistakes you can make.
What Are the Biggest Mistakes New Traders Make?
It's almost uncanny how new traders fall into the same handful of traps. If you know what they are from day one, you stand a much better chance of sidestepping them.
These are the big ones I see over and over again:
- Terrible Risk Management: This is the king of all mistakes. Risking way too much per trade and ignoring the 1% rule is the fastest ticket to a zero balance.
- Trading on Emotion: You just took a frustrating loss. The urge to jump right back in to "win your money back" is intense. That's "revenge trading," and it's a disaster waiting to happen.
- Having No Plan: If you enter the market without a clear reason, a target for your profit, and a point where you'll cut your losses, you aren't trading. You're gambling.
- Overtrading: So many beginners feel like they have to be in a trade constantly to make money. The truth is, most of my time as a trader is spent waiting patiently for the perfect setup. The waiting is the work.
Steering clear of these fundamental errors is what will keep you in the market long enough to actually learn, grow, and succeed.
Ready to build the right habits from the start? At Colibri Trader, we focus on a straightforward, price-action-based approach to help you trade with confidence and consistency. Learn more about our action-based programs and start your journey at https://www.colibritrader.com.