How to Do Forex Trading A Guide for Ambitious Beginners
Diving into the world of forex can feel like learning a whole new language, but figuring out how to do forex trading is a lot more straightforward than most people think.
It all boils down to a few key things: getting a handle on the basics, finding a broker you can trust, hammering out a solid trading plan, and finally, having the confidence to place that first trade. This is the path every single successful trader has walked. No exceptions.
Your First Steps into the World of Forex Trading

Welcome to the foreign exchange market. It's the biggest, most liquid financial playground on the planet, and its sheer size is hard to wrap your head around.
As of early 2025, the forex market is seeing an average daily trading volume of around $7.5 trillion. To put that in perspective, it makes the Nasdaq's $200 billion daily average look tiny. This massive liquidity is a huge advantage for new traders because it means there's almost always a buyer when you want to sell, and a seller when you want to buy.
Before you jump in, it’s absolutely critical to understand the foundational terms of forex trading. These concepts are the bedrock of every decision you'll make.
Here's a quick summary to get you started.
Core Forex Trading Concepts at a Glance
| Concept | What It Means for a Trader | Practical Example |
|---|---|---|
| Currency Pairs | You're always trading one currency against another, betting on which one will get stronger or weaker. | In the EUR/USD pair, you're speculating on the Euro's value relative to the U.S. Dollar. |
| Pips | This is the tiny unit of measurement for price changes. It's how you count your profits or losses. | If EUR/USD moves from 1.0850 to 1.0851, that’s a one-pip increase. |
| Leverage | A tool from your broker that lets you control a large position with a small amount of capital. It’s powerful. | With 100:1 leverage, you can control a $100,000 position with just $1,000 in your account. |
Grasping these terms is your first step. It ensures you're not just guessing but making calculated moves based on real market mechanics.
Grasping the Core Concepts
Before you even think about risking a single dollar, you have to learn the language of the market. I'm not talking about complex algorithms—just the fundamental building blocks that govern every single trade. It's like learning the rules of a new sport before stepping onto the field.
These concepts are your starter toolkit for making sense of the charts:
- Currency Pairs: Forex is always traded in pairs, like the classic EUR/USD (Euro vs. U.S. Dollar). You're speculating that one currency's value will rise or fall against the other. Simple as that.
- Pips (Percentage in Point): This is the standard unit we use to measure a change in value. For most pairs, a move from 1.0850 to 1.0851 is a one-pip move. It's how we keep score.
- Leverage: This is a tool brokers offer that lets you control a large position with a small amount of your own money. It can seriously amplify your profits, but it also magnifies losses. Treat it like a double-edged sword that demands respect and careful handling.
Understanding What Moves the Market
Currency prices don't just move randomly. They react to a mix of economic data releases, geopolitical news, and the overall mood of the market. For instance, when a country's central bank decides to raise interest rates, its currency often gets stronger because it offers a better return for investors.
The real skill in forex trading isn't just knowing these concepts, but understanding how they interconnect to tell a story about market direction. Your job is to read that story and make educated predictions.
A solid grasp of these drivers is what separates informed speculation from just gambling. It gives you the power to build a real reason—a thesis—for why a trade might work out, moving you way beyond just blindly clicking "buy" or "sell."
The Power of a Trading Plan
I can tell you this from experience: no professional trader I know goes into the market without a clear set of rules. A trading plan is your personal business plan for trading. It spells out exactly what you'll trade, when you'll trade it, and most importantly, how you'll manage your risk on every single position.
This plan is your best defense against emotional decisions and sloppy, undisciplined actions—the two main reasons most new traders wash out. It gives you structure and takes the guesswork out of the equation.
For anyone who's ready to get serious, our guide on how to make a forex trading plan in 10 steps is an absolutely essential resource for building this critical foundation.
Choosing the Right Broker and Trading Platform

Think of your broker as your direct gateway to the forex market. This isn't a choice to take lightly; it's one of the most important decisions you'll make in your trading journey. The right partner can make your life a lot easier, while the wrong one can introduce a world of headaches and unnecessary risk.
Your first and most critical checkpoint is regulation. I can't stress this enough: a broker must be regulated by a top-tier financial authority. This is completely non-negotiable. These agencies enforce strict rules to protect your capital from fraud or mismanagement, ensuring your funds are held in segregated accounts, separate from the broker’s operational cash.
Verifying Broker Regulation
Before you even glance at fees or fancy platforms, confirm the broker's regulatory status. You're looking for oversight from reputable bodies like:
- Financial Conduct Authority (FCA) in the United Kingdom
- Australian Securities and Investments Commission (ASIC) in Australia
- Cyprus Securities and Exchange Commission (CySEC) in Cyprus
A genuinely regulated broker will proudly display its license number on its website, usually in the footer. You can—and absolutely should—verify this number directly on the regulator's official online register. If you can't find it, or if it doesn't check out, walk away immediately. It's that simple.
Your capital's safety is priority number one. Strong regulation is the single most important factor because it provides a layer of security and accountability that is otherwise absent.
Decoding the Fee Structures
Once you've confirmed regulation, the next thing to look at is cost. Brokers make money in two primary ways: through spreads or through commissions. Understanding the difference is key to knowing what you're actually paying.
A spread is the tiny difference between the buy (ask) price and the sell (bid) price of a currency pair. This is the most common fee model you'll see. For example, if the EUR/USD bid is 1.0850 and the ask is 1.0851, the spread is one pip. You pay this spread on every single trade you make.
A commission-based model often offers much tighter—sometimes near-zero—spreads. In return, you pay a fixed fee per trade, like $3 per lot (which is 100,000 units of currency). This structure can be a lot more cost-effective if you plan on being a high-volume trader.
Comparing Spreads vs. Commissions
| Fee Model | How It Works | Best For |
|---|---|---|
| Spreads | The broker profits from the difference between buy and sell prices. | Beginners and lower-volume traders who prefer simplicity and no separate fees. |
| Commissions | The broker charges a flat fee per trade, offering very tight spreads in return. | Active, high-volume traders who can benefit from lower per-trade costs over time. |
Test Drive with a Demo Account
Never, ever deposit real money without first test-driving the broker's platform with a demo account. A demo account is a risk-free simulator that uses virtual money but real-time market data. It’s the perfect way to get a real feel for the platform’s layout, execution speed, and tools without putting a single dollar on the line.
This is your chance to practice placing trades, setting stop-loss orders, and customizing your charts. I recommend spending at least a few weeks in a demo environment to build confidence and make sure the platform suits your trading style before you even think about going live.
Navigating Trading Platforms
Your broker provides the technology, but the trading platform is where you'll spend your time analyzing charts and executing trades. The undisputed king in the retail forex world is MetaTrader 4 (MT4).
The forex market is massive, with an estimated annual turnover of $2.4 quadrillion. Platforms like MT4 are what make this giant market accessible to regular people like us. In fact, an estimated 85% of traders use MT4, making it the global standard. What’s great about this popularity is the massive community and countless free resources out there to help you master it. You can find more staggering data on the forex market's incredible size at The Tokenist.
When you first open a platform like MT4, you'll see a few key components:
- Market Watch: A running list of currency pairs with their live bid and ask prices.
- Chart Window: The main screen where you'll see the price action for a selected pair. This is where you'll do your analysis.
- Navigator: Your access point for indicators, expert advisors (trading bots), and your different accounts.
- Terminal: Shows your open trades, account balance, profit/loss, and trading history.
Get comfortable with these different windows in your demo account. Learning to navigate your platform efficiently is a fundamental skill that directly impacts your ability to react to market opportunities quickly and accurately.
Building Your First Simple Trading Strategy

Jumping into the market without a strategy is like driving blind. You're just gambling, and I've seen it wipe out countless new traders who let emotion call the shots. The goal isn't to guess; it's to trade with a clear set of rules.
You don’t need a PhD in economics or a screen full of flashing indicators to get started. Honestly, some of the most reliable strategies I've used are incredibly simple. They're built on price action—the skill of reading the market's story right from a clean price chart.
Finding Support and Resistance Levels
First things first, you need to map out the battle lines on your chart. These are your support and resistance levels. Think of them as psychological fences where either buyers or sellers have historically shown up in force.
- Support: This is a price floor. It's an area where falling prices tend to stop and bounce because buyers see value and step in.
- Resistance: This is a price ceiling. It's a level where rising prices often stall out as sellers take profits or initiate short positions.
To find them, just look for horizontal zones on your chart where the price has reversed multiple times. The more a level is tested and holds, the more significant it becomes. These are the logical spots to plan your trades.
A huge piece of the puzzle is understanding that when a key level breaks, roles can flip. Old support can become new resistance, and old resistance can become new support. A breakout isn't just a line being crossed; it's a major shift in market sentiment.
Reading the Story with Candlestick Patterns
Once you have your key levels marked, you need to look for clues about who's winning the current fight between bulls and bears. This is where candlestick patterns are pure gold. Each candle tells you the story of what happened during that specific time frame.
A candlestick chart shows you the open, high, low, and close prices, giving you an immediate visual cue about market sentiment.

The image above breaks down the anatomy of bullish (green/white) and bearish (red/black) candles. Getting familiar with these is your first step to seeing the more complex stories—the patterns—play out.
One of the most powerful patterns, and one that’s easy to spot, is the Engulfing Bar.
- A Bullish Engulfing Bar happens when a big bullish candle completely swallows the previous, smaller bearish candle. Spotting this at a strong support level is a classic sign that buyers have just seized control.
- A Bearish Engulfing Bar is the opposite. A big bearish candle completely engulfs the prior bullish one. When this happens near a resistance level, it’s a strong signal that sellers have taken over.
When an engulfing bar forms right at one of your pre-identified support or resistance levels, that's a high-probability trade signal you should pay close attention to.
Adding a Layer of Confirmation with Moving Averages
To give your strategy an extra dose of confidence, you can use a simple tool to confirm the market's overall direction: the Moving Average (MA). An MA smooths out the chaotic price wiggles into a single, flowing line, making the underlying trend much easier to see.
A very common and effective setup is using two MAs: a fast one (like a 20-period MA) and a slow one (like a 50-period MA).
- Uptrend Confirmation: When the faster 20 MA crosses above the slower 50 MA, and both are pointing up, it reinforces a bullish trend.
- Downtrend Confirmation: When the 20 MA crosses below the 50 MA, and both are angled down, it helps confirm a bearish trend.
Now, you can put it all together. For instance, you could decide to only look for bullish engulfing patterns at support levels if the 20 MA is trading above the 50 MA. This simple filter keeps you trading with the primary trend, which is one of the smartest things a new trader can do.
This price action approach is just one of many ways to read the market. To broaden your horizons, I recommend checking out this great breakdown of 7 forex trading strategies every trader must know to find what clicks with your personality. The real secret is finding a simple, repeatable process and having the discipline to stick to it.
Mastering Risk Management to Protect Your Capital
In the world of forex trading, your survival doesn't depend on how much you make when you're right. It's about how little you lose when you're wrong. This isn't just a catchy phrase; it's the single most important philosophy that separates the pros from the crowd. Solid risk management is the absolute bedrock of a lasting trading career.
Forget about hitting home runs. Your primary job, above all else, is to protect your capital. The traders who are still around to see success are the ones who obsess over defense, making damn sure that no single trade—or even a string of bad trades—can knock them out of the game.
The Non-Negotiable Stop-Loss Order
Your most powerful defensive tool is the stop-loss order. Simple. It's an order you place with your broker to automatically kill a losing trade once it hits a price level you've decided on beforehand. It’s your safety net. It’s your emergency exit. And using one on every single trade is not optional. It's mandatory.
Picture this: you go long on EUR/USD at 1.0850, convinced it's heading up. Without a stop-loss, a surprise news event could crater the price to 1.0700 while you're grabbing lunch, wiping out a huge chunk of your account. But with a stop-loss set at 1.0820, your loss is capped. Contained. Manageable. It's how you enforce discipline when your emotions want to take over.
The One Percent Rule: Your Trading Lifeline
So, how do you decide where to place that stop-loss? It all starts with the 1% rule, a true cornerstone of capital preservation. The rule is incredibly simple but profoundly effective: you should never risk more than 1% of your total account balance on a single trade.
If you have a $5,000 trading account, this means the absolute most you can lose on any one idea is $50. This isn't just about limiting the financial damage; it's about managing the psychological pressure that sinks so many traders.
- Keeps Emotions in Check: When you know your maximum loss is a small, manageable number, you’re far less likely to make panicked, irrational decisions.
- Ensures Survival: Think about it. Even a disastrous streak of ten consecutive losses would only draw your account down by about 10%. You'd still have plenty of capital left to fight another day.
- Forces Discipline: This rule forces you to be selective. You can't just jump on any setup; you have to find trades that fit your strict risk parameters.
By sticking religiously to the 1% rule, you shift your entire focus from chasing profits to controlling risk. That mental switch is what opens the door to long-term consistency and growth in the forex market.
Calculating Your Risk-to-Reward Ratio
Once you know your risk, you need to look at the other side of the coin: the potential reward. This brings us to the risk-to-reward ratio. It's just a simple comparison of what you're risking (the distance from your entry to your stop-loss) to what you stand to gain (the distance to your profit target).
A common minimum standard among seasoned traders is a 1:2 risk-to-reward ratio. In plain English, for every $1 you risk, you should be aiming to make at least $2 in profit.
Let's walk through a real-world scenario. You spot a potential long trade on GBP/USD at 1.2500. Your analysis tells you that a logical place for your stop-loss is 1.2450, putting 50 pips at risk. To meet that 1:2 ratio, your profit target needs to be at least 100 pips away, up at 1.2600.
Why is this so powerful? With a 1:2 ratio, you only need to be right 34% of the time to break even. Any win rate higher than that, and you're profitable. This framework gives you the breathing room to be wrong more often than you are right and still grow your account. To truly excel, you must master the risk-reward ratio calculation for every single trade you even consider taking.
All the theory is behind you and your demo account is fired up. Now it's time to connect the dots between what you know and what you do. This is the moment you bring your strategy, risk management, and platform skills together to pull the trigger on your first trade.
Let's walk through a real-world scenario so you can see exactly how to do forex trading in practice, from start to finish.
Imagine you've got the EUR/USD chart open. Your price action strategy has helped you spot a rock-solid support level at 1.0800. The pair has been selling off, but right at that support level, a big, clear bullish engulfing candle prints. That's a classic signal that buyers are jumping in with some serious muscle. Your moving averages are also hinting at a potential change in direction. This is it—your trade signal.
Executing the Trade Step by Step
This is where your trading plan takes over. And believe it or not, the first decision isn't about how much you can make; it's about how much you're willing to lose.
Let's say you're working with a $2,000 demo account. Sticking to the 1% rule, your absolute maximum risk on this single trade is $20. No more.
You decide to place your protective stop-loss just underneath the low of that bullish engulfing candle, maybe at 1.0780. This gives the trade a bit of breathing room but clearly defines your line in the sand. The distance from your entry (let's say you get in at 1.0805) to your stop-loss (1.0780) is 25 pips.
Now it’s time to figure out your position size. With your risk capped at $20 and your stop-loss distance at 25 pips, you need to calculate a lot size where a 25-pip move against you equals exactly a $20 loss. Don't worry, your platform's built-in calculators are perfect for this. Once you have the right position size, you're ready to go.
You'll place three distinct orders:
- Entry Order: A buy order right now, at the market price of 1.0805.
- Stop-Loss Order: An automatic sell order that triggers if the price drops to 1.0780, protecting you from further losses.
- Take-Profit Order: You're shooting for at least a 1:2 risk-to-reward ratio, so you set your profit target 50 pips above your entry, at 1.0855.
This whole structured process is how you manage your risk before you even click the buy button.
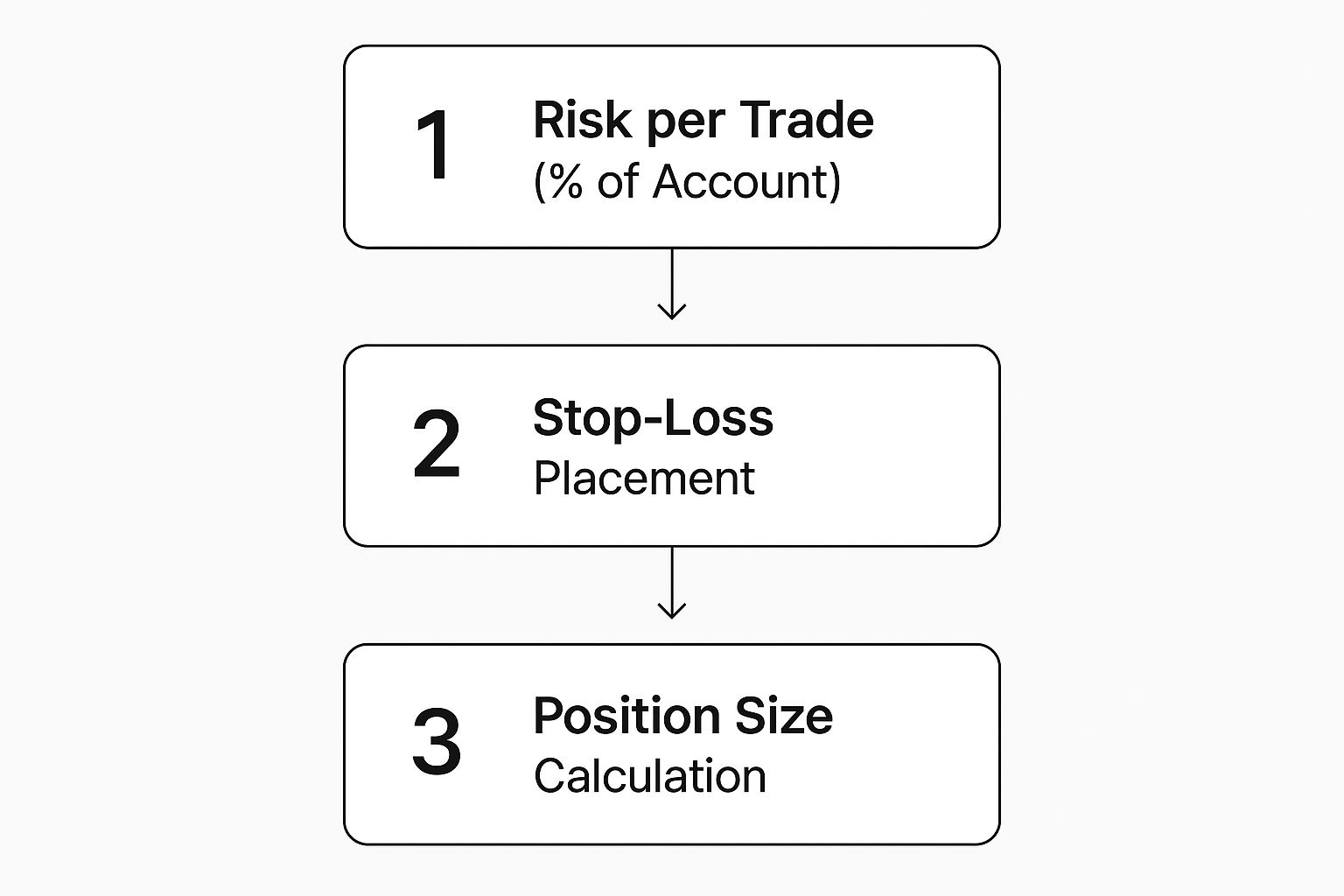
This workflow shows something crucial: calculating your position size is the last thing you do. It's dictated entirely by your pre-planned risk and your strategic stop-loss placement.
The Power of a Trading Journal
Once your trade is closed—win or lose—the real work begins. This single habit is what separates traders who get better from those who spin their wheels for years. You need to keep a trading journal. And no, this isn't just a boring log of wins and losses. It’s your tool for brutally honest self-analysis.
Your journal is where you become your own trading coach. For every single trade, you have to document the "why." What was the setup? Why did you enter? Did you follow your plan to the letter? How did you feel when you were in the trade?
A trading journal is the ultimate accountability tool. It forces you to confront your mistakes, recognize your strengths, and see the patterns in your own behavior that you would otherwise miss.
This is how you shine a light on your psychological gremlins. Are you constantly cutting winning trades short because you're scared of giving profits back? Are you nudging your stop-loss further away because you can't stomach being wrong? Your journal will show you the unfiltered truth.
Remember, the global forex market is a massive, complex machine. To give you some perspective, in 2023-2024, London remained the world's biggest forex hub, where instruments like forex swaps made up a staggering 46% of its daily turnover. This shows just how deep the market is. To learn more about the ecosystem you're trading in, check out these insights on global forex market dynamics.
A Simple Journal Template to Start
You don't need fancy software. A simple spreadsheet is all it takes. Just create a few columns to track the most important data points so you can analyze your performance over time.
Essential Trading Journal Fields
| Column | Purpose |
|---|---|
| Date/Time | Record when you opened and closed the trade. |
| Currency Pair | Note the pair you traded (e.g., EUR/USD). |
| Setup/Strategy | Describe your reason for the trade (e.g., "Bullish engulfing at support"). |
| Entry & Exit Price | The exact prices where you got in and out. |
| Stop-Loss Price | The price of your initial protective stop order. |
| Profit/Loss (Pips) | The trade outcome measured in pips. |
| Profit/Loss ($) | The trade outcome in dollars and cents. |
| Notes/Emotions | Your thoughts and feelings. Were you patient, fearful, greedy, or bored? |
Make it a non-negotiable habit to review your journal every week. Look for patterns. Are you always losing money on a certain currency pair? Is there one specific setup that's a consistent winner for you? This feedback loop is the engine that drives improvement, helping you sharpen your strategy and build discipline, one trade at a time.
Your Top Forex Trading Questions Answered
When you're just starting out in forex, it's natural to have a ton of questions. I know I did. Getting solid, straight-up answers is one of the first steps to building the confidence you need to trade the right way.
Let's cut through the noise. Here are the questions I hear most often from new traders, along with the no-fluff answers you need.
How Much Money Do I Really Need to Start Trading Forex?
You'll see brokers letting you open an account with just $100. Technically, you can, but I wouldn't recommend it. A much more practical starting point is somewhere between $500 and $1,000.
Why that amount? It's not some random number. It's about giving yourself enough room to breathe and apply proper risk management. With a tiny account, it's almost impossible to follow something like the 1% rule without every single trade being a massive gamble relative to your capital. That kind of pressure is a recipe for disaster and builds terrible habits.
My best advice? Forget real money for a while. Prove your strategy actually works on a demo account first. Once you have a profitable track record there, then you can think about funding a live account.
What Is the Best Currency Pair for Beginners?
Keep it simple and stick to the major currency pairs. These are the most heavily traded pairs in the world, which means they have the highest liquidity and, crucially, the tightest spreads. Tighter spreads mean lower trading costs for you.
The EUR/USD is the classic starting point for a reason. Its massive trading volume generally leads to smoother, more predictable price movements than you'll see in other pairs.
A few other solid choices for beginners are:
- GBP/USD (British Pound vs. U.S. Dollar)
- USD/JPY (U.S. Dollar vs. Japanese Yen)
Whatever you do, stay far away from the exotic pairs (like USD/TRY or EUR/ZAR) when you're new. Their wild volatility and much wider spreads can chew up a small account in no time.
The reality is that the vast majority of successful retail traders are self-taught. True competence comes from screen time, disciplined practice, and meticulously learning from your own trades—not from a secret formula someone is selling.
Can I Actually Teach Myself to Trade Forex?
Yes, without a doubt. Success in trading comes down to a structured, disciplined approach—not from some expensive course promising you the world.
Pour your energy into mastering one simple, repeatable strategy. Make risk management your number one job. And use that demo account like it's your full-time profession. The journey is all about consistent effort and brutally honest self-analysis of your trades, win or lose.
How Long Does It Take to Become a Profitable Trader?
There is no set timeline, and anyone who tells you otherwise is selling something. Realistically, it takes most traders one to two years of consistent learning, disciplined practice, and getting their emotions in check before they see steady profitability.
Be extremely skeptical of anyone promising you can get rich in a few weeks or months. That's just not how this works.
Ultimately, your success will have far more to do with your psychological discipline and commitment than your raw market knowledge. Treat it like a marathon, not a sprint. Focus on getting a little better every single day.
Ready to stop gambling and start trading with a proven, rule-based approach? At Colibri Trader, we teach you the price action skills to trade confidently without relying on confusing indicators. Transform your performance and find consistency in the markets. Take our free Trading Potential Quiz today!