Top 10 Price-Action Tips for the Best Trading Strategy in 2025
The quest for the best trading strategy is universal, but the answer is deeply personal. A high-frequency algorithm that thrives on volatility might bankrupt a patient, long-term investor. The secret isn't finding a mythical, one-size-fits-all method; it's about discovering a system that aligns perfectly with your personality, risk tolerance, and available time commitment. Success in the markets comes from matching your unique psychological makeup to a specific market approach.
This guide is designed to demystify that process. We will break down 10 powerful and distinct trading strategies, with a practical focus on price-action techniques that don't rely on lagging indicators. Instead of abstract theory, you will get a direct, side-by-side comparison of how each strategy works, its ideal market conditions, and its specific advantages and disadvantages. We’ll explore trend following, swing trading, scalping, and more, giving you the essential details needed to make an informed choice.
By the end of this article, you will have a clear framework for identifying, testing, and implementing a trading strategy that gives you a genuine, repeatable edge. This is not about finding a "holy grail" but about building a robust, personalized process for achieving consistent results. You will learn to move beyond random trades and begin operating with a defined plan that fits who you are as a trader, whether you're a novice just starting or an experienced professional looking to refine your approach.
1. Trend Following Strategy
The Trend Following Strategy is arguably one of the most intuitive and enduring approaches to the markets, making it a strong contender for the best trading strategy for both new and experienced traders. Its core principle is simple: “the trend is your friend.” Instead of predicting market tops or bottoms, traders using this method identify an established directional move and ride it for as long as it lasts. The fundamental belief is that markets have momentum, and an asset in motion is more likely to stay in motion than to reverse course.
How It Works
A trend follower's primary job is to identify a clear uptrend (a series of higher highs and higher lows) or a downtrend (lower lows and lower highs) and enter a position in that direction. Success doesn't come from a high win rate; in fact, many trend followers win on less than 50% of their trades. Profitability comes from letting winning trades run to capture significant gains while cutting losing trades short with disciplined stop-losses. This asymmetrical risk-reward profile is the engine of the strategy.
For a practical example, consider a classic moving average crossover. A trader might buy a stock when its 50-day moving average crosses above the 200-day moving average, signaling a new uptrend. They would hold this position until the 50-day average crosses back below the 200-day, signaling the trend's end. The legendary Turtle Traders, taught by Richard Dennis, famously used a similar system based on breakouts to new highs to amass fortunes.
This summary box provides a quick reference for the core components of the Trend Following Strategy.
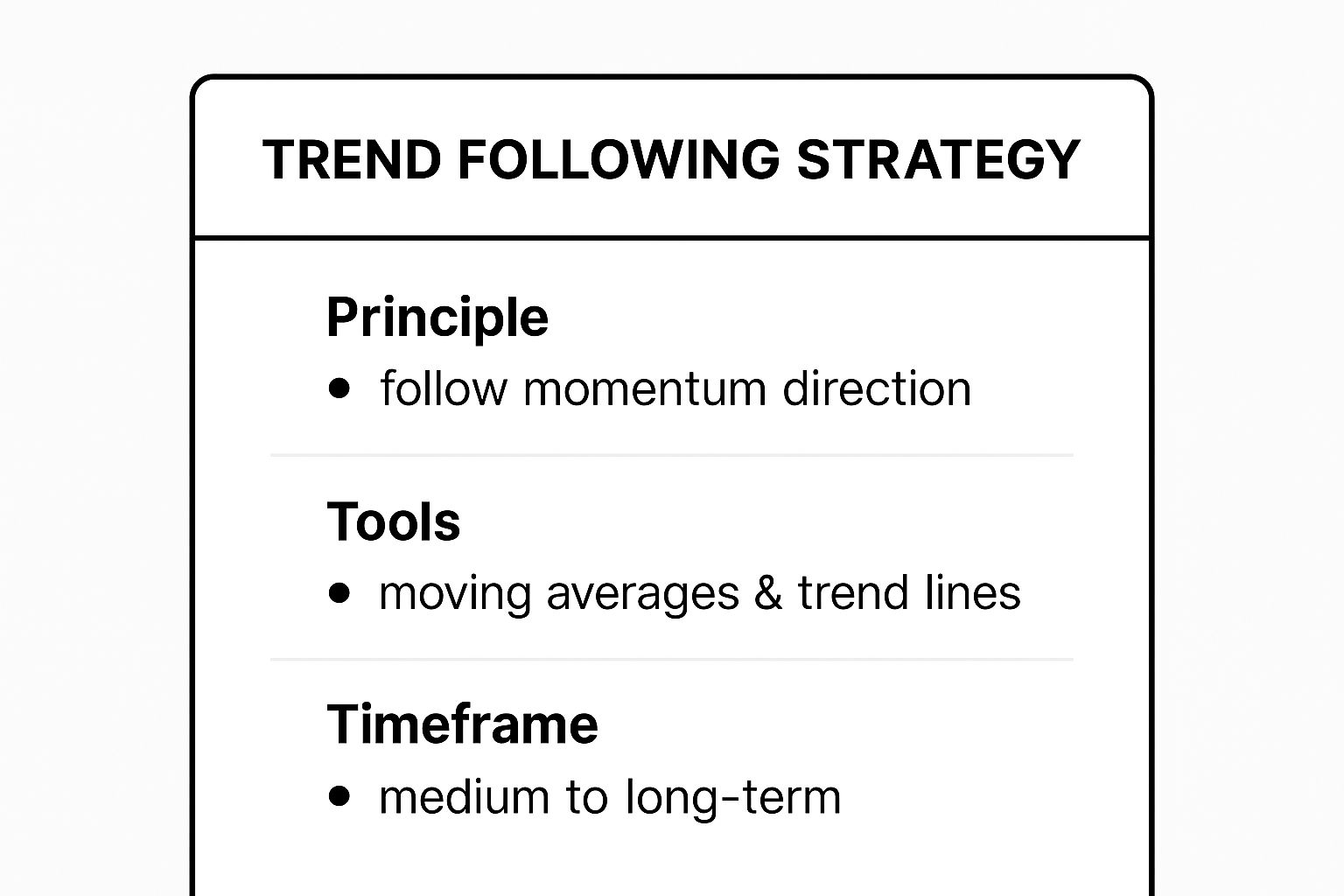
As the infographic highlights, the strategy is built on following momentum over longer timeframes using simple but effective tools.
Actionable Tips for Implementation
To effectively implement this strategy, focus on discipline and structure.
- Confirm with Multiple Timeframes: A strong trend should be visible on more than just one chart. If you see an uptrend on the daily chart, check the weekly chart to confirm the larger directional bias.
- Use Trend Strength Indicators: Tools like the Average Directional Index (ADX) can help you avoid weak, choppy markets. A rising ADX above 25 often indicates a strong, tradable trend.
- Master Market Structure: Understanding the sequence of peaks and troughs is crucial for identifying trends. You can learn more about how to define market structure on colibritrader.com to enhance your trend analysis.
- Embrace Patience: Trend following requires immense patience. There will be long periods of sideways market action where no clear signals emerge. Resisting the urge to trade during these times is key to preserving capital.
2. Swing Trading Strategy
The Swing Trading Strategy is a highly popular approach that seeks a middle ground between the frantic pace of day trading and the long-term commitment of position trading, making it a versatile contender for the best trading strategy. Its core principle is to capture price “swings” or momentum bursts that occur over several days to several weeks. Swing traders aren't trying to catch the entire trend; instead, they aim to profit from the smaller up and down movements within a larger market trend.

How It Works
Swing traders use technical analysis to identify potential entry and exit points based on price action and key indicators. They look for established trends and then wait for short-term counter-movements, or pullbacks, to enter a trade. The goal is to enter just as the price is about to resume its primary direction, capturing the subsequent "swing" higher or lower. This method requires less screen time than day trading but more active management than long-term investing.
A practical example would be identifying a strong uptrend in a stock like Microsoft. A swing trader would wait for the price to pull back to a key support level, such as the 50-day moving average or a previous resistance-turned-support zone. They would enter a long position once they see signs of the pullback ending (e.g., a bullish candlestick pattern) and place a stop-loss just below that support level. Their profit target might be the previous high or a key resistance level, allowing them to exit the trade after capturing a multi-day move.
Actionable Tips for Implementation
To effectively implement swing trading, focus on identifying high-probability setups and managing risk meticulously.
- Master Support and Resistance: These levels are the roadmap for swing traders. Use them to identify logical entry points, place stop-losses, and set realistic profit targets.
- Focus on Liquid Markets: Stick to assets with high trading volume, like major currency pairs (EUR/USD) or large-cap stocks. Liquidity ensures you can enter and exit trades efficiently without significant price slippage.
- Use Catalysts as Confirmation: For stocks, a fundamental catalyst like an earnings report or an FDA announcement can fuel a powerful swing. Use these events to anticipate increased volatility and trading opportunities.
- Keep a Trading Journal: Meticulously track every trade, noting your entry/exit points, the reason for the trade, and the outcome. This practice is crucial for identifying patterns in your performance and refining your strategy over time. To better understand its unique timeline, you can learn more about the differences between day trading and swing trading at colibritrader.com.
3. Scalping Strategy
The Scalping Strategy is a high-octane approach that represents the opposite end of the spectrum from trend following, making it a powerful contender for the best trading strategy for those who thrive on action. Its core principle is to capture numerous small profits from minimal price fluctuations. Instead of waiting for large market moves, scalpers enter and exit trades within seconds or minutes, aiming to capitalize on the constant ebb and flow of the market. The fundamental belief is that smaller, frequent gains can compound into significant profits over a trading session.

How It Works
A scalper's main objective is to exploit the bid-ask spread or small, predictable price movements that occur throughout the day. Success is not derived from large winning trades but from a high win rate combined with rigid risk management. Profitability comes from the cumulative effect of many small wins, while losses are kept minuscule with extremely tight stop-losses. This high-volume, low-margin approach demands intense focus and rapid decision-making.
For a practical example, a forex scalper might trade the EUR/USD pair during the London-New York session overlap when volatility is high. They might enter a long position based on order flow data, aiming for a 5-pip profit and setting a stop-loss just 3 pips away. The position is often closed within a minute. Legendary traders like Paul Rotter became famous for executing thousands of such trades daily in the futures markets, building their fortunes one tick at a time.
Actionable Tips for Implementation
To effectively implement this strategy, focus on precision, speed, and unwavering discipline.
- Choose High-Liquidity Markets: Focus on assets with tight spreads and high trading volume, like major forex pairs or E-mini S&P 500 futures. This ensures you can enter and exit trades instantly without significant slippage.
- Utilize Level 2 Market Data: Level 2 (market depth) data shows you the order book, providing insight into supply and demand dynamics. This can give you an edge in predicting short-term price movements for better entry and exit timing.
- Maintain Ironclad Discipline: Scalping is unforgiving. Predetermine your profit and loss targets for every trade and stick to them without hesitation. You can learn how to set a stop-loss effectively on colibritrader.com to master this critical skill.
- Ensure a Rock-Solid Setup: A fast, reliable internet connection and a robust trading platform are non-negotiable. Lag or system freezes can turn a winning trade into a significant loss in seconds.
4. Mean Reversion Strategy
The Mean Reversion Strategy operates on a principle that is the polar opposite of trend following, making it another powerful contender for the best trading strategy. Its core assumption is that markets are cyclical and that extreme price moves are temporary. The fundamental belief is that asset prices and historical returns will eventually revert to their long-term average or mean. This creates opportunities to trade against the prevailing short-term momentum.
How It Works
A mean reversion trader’s primary goal is to identify assets that have stretched too far from their historical average, either to the upside or downside, and place a trade in the opposite direction. This strategy bets on the "rubber band effect" where the further a price stretches, the more forcefully it's likely to snap back. Profitability comes from capturing these corrections, often resulting in a high win rate but smaller individual profits compared to trend following.
For a practical example, consider a highly correlated pair of stocks like Coca-Cola and Pepsi. If the price ratio between them deviates significantly from its historical average (e.g., Pepsi becomes unusually expensive relative to Coke), a pairs trader might short Pepsi and buy Coke. They would hold this position until the ratio reverts to its mean, profiting from the correction. Similarly, traders might sell volatility by shorting the VIX when it spikes to extreme highs during a market panic, anticipating its inevitable return to lower levels.
Actionable Tips for Implementation
To effectively implement this strategy, focus on statistical evidence and risk management.
- Use Statistical Bands: Tools like Bollinger Bands or Keltner Channels provide a visual representation of an asset's average and its standard deviation. A price touching or exceeding the outer bands can signal an overextended move ripe for a reversal.
- Focus on Range-Bound Assets: This strategy works best on assets that have a history of trading within a predictable range, such as certain currency pairs or stocks in mature, stable industries. Avoid applying it to strong, trending markets.
- Set Strict Risk Parameters: Mean reversion can be dangerous if a new trend forms instead of a reversal. Always use a hard stop-loss to protect against a "fade" trade that turns into a runaway loss.
- Be Aware of Catalysts: Major news, earnings reports, or economic data can permanently alter an asset's perceived value, breaking its historical mean. Avoid entering mean reversion trades right before such events.
5. Breakout Trading Strategy
The Breakout Trading Strategy is a powerful method centered on capturing significant price moves that occur after an asset breaks through a key level of support or resistance. This approach is built on the idea that periods of market consolidation, where price is trapped in a range, eventually resolve with an explosive directional move. For many, this is a top contender for the best trading strategy because it capitalizes on shifts in market sentiment and momentum.
How It Works
A breakout trader's primary task is to identify well-defined boundaries, such as support and resistance levels, chart patterns like triangles or flags, or price channels. The trader then waits for the price to decisively move beyond this boundary, often accompanied by a surge in trading volume, which confirms the conviction behind the move. The goal is to enter a trade just as the breakout occurs, positioning to ride the subsequent momentum. Unlike trend followers who join an existing move, breakout traders aim to be among the first to catch a new one.
For example, if a stock has repeatedly failed to rise above $105 (a resistance level) but finally closes above it on high volume, a breakout trader would enter a long position. The expectation is that the previous barrier has been broken, clearing the path for a significant upward move. This method was a core component of Nicolas Darvas's "Box Theory" and is used extensively by modern traders like Mark Minervini to capture powerful earnings-driven moves.
Actionable Tips for Implementation
To effectively implement this strategy, focus on confirmation and risk management.
- Wait for Volume Confirmation: A breakout on low volume is often a "fakeout" or a false signal. A significant increase in volume suggests strong institutional participation and adds validity to the move.
- Validate on Multiple Timeframes: A breakout that is visible on both a 4-hour and a daily chart is far more reliable than one that only appears on a 5-minute chart. The higher timeframe confirms the significance of the broken level.
- Set Protective Stop-Losses: A crucial rule is to place your stop-loss just below the resistance level you bought above, or just above the support level you sold below. This ensures a quick exit if the breakout fails.
- Focus on Established Levels: The most powerful breakouts occur from levels that have been tested multiple times. The more a level has held in the past, the more significant its eventual break will be.
6. Momentum Trading Strategy
The Momentum Trading Strategy is a dynamic approach built on the idea that assets performing well will continue to perform well, and those performing poorly will continue to do so. Its central principle is to buy high and sell higher. Instead of seeking undervalued assets, momentum traders capitalize on market psychology and institutional flows that often push strong price movements further in their existing direction. The strategy assumes that strong trends, once established, possess inertia.
How It Works
A momentum trader's goal is to identify stocks or other assets exhibiting strong directional price movement accompanied by high volume and then ride that momentum until signs of reversal appear. This is a very active strategy that requires constant monitoring. Profitability stems from capturing powerful, short-to-medium-term price swings. Unlike trend followers who may hold positions for months, momentum traders often operate on timeframes ranging from a few days to several weeks.
A practical example is identifying a stock that has just broken out of a consolidation range on significantly higher-than-average volume, perhaps driven by a positive earnings report. A momentum trader would buy into this strength, placing a tight stop-loss. They would hold the position as long as the price continues to make new highs, often using a trailing stop-loss to lock in profits as the trade moves in their favor. The CANSLIM methodology, developed by William O'Neil, incorporates momentum as a key factor in stock selection.
Actionable Tips for Implementation
To effectively implement this strategy, focus on speed, risk management, and identifying the right catalysts.
- Use Relative Strength Indicators: Tools like the Relative Strength Index (RSI) or simply comparing a stock's performance to a benchmark index (like the S&P 500) can help you quickly identify market leaders showing superior momentum.
- Focus on Volume: Genuine momentum is almost always confirmed by a surge in trading volume. A price breakout on low volume is often a red flag and may not have the conviction to continue.
- Set Trailing Stops: Since momentum can reverse sharply, using a trailing stop-loss is crucial. This technique automatically adjusts your stop-loss order upwards as the price rises, protecting your profits without capping your potential upside.
- Scan for Catalysts: Be aware of news, earnings reports, or industry-wide developments that can initiate or sustain momentum. Strong fundamental drivers often create the most powerful and lasting price moves.
7. Arbitrage Trading Strategy
The Arbitrage Trading Strategy is unique because it seeks to generate profit from market inefficiencies rather than from predicting market direction. It is considered one of the few theoretically risk-free approaches to trading. The core principle is to simultaneously buy and sell the same asset in different markets to capitalize on a temporary price difference. This strategy relies on the law of one price, which states that an asset should cost the same everywhere, and arbitrageurs profit when this law is temporarily broken.
How It Works
An arbitrageur's goal is to identify a price discrepancy for an identical asset across two or more exchanges, brokers, or markets. Once found, they execute a buy order on the market with the lower price and a simultaneous sell order on the market with the higher price. The difference, minus any transaction costs, is their profit. Success depends almost entirely on speed and access to sophisticated technology, as these price differences are often minuscule and last for mere milliseconds before other market participants erase them.
For example, imagine a stock is trading for $100.50 on the New York Stock Exchange but for $100.55 on the BATS exchange at the same instant. An arbitrage trader would simultaneously buy the stock on the NYSE and sell it on BATS, locking in a $0.05 per-share profit. While this seems small, high-frequency trading (HFT) firms execute millions of such trades daily, turning tiny profits into substantial sums. This constant activity is also what makes markets more efficient, quickly correcting these pricing errors.
Actionable Tips for Implementation
Due to its technological demands, pure arbitrage is challenging for retail traders but the principles are valuable.
- Invest in Low-Latency Technology: The foundation of modern arbitrage is speed. Professional firms use co-location services to place their servers in the same data centers as exchanges to minimize execution delays.
- Monitor Multiple Markets Simultaneously: You need a system that can scan and compare real-time price feeds from numerous venues at once to spot discrepancies as they appear.
- Factor In All Transaction Costs: Profits are often razor-thin. It's critical to calculate exchange fees, broker commissions, and any other costs to ensure a trade is actually profitable before executing.
- Explore Statistical Arbitrage: A more accessible form for retail traders is statistical arbitrage, which uses quantitative models to find price relationships between different but related assets (like a pair of stocks in the same sector) and trades them when their prices diverge from their historical correlation.
8. Position Trading Strategy
Position Trading is a long-term strategy that stands in stark contrast to the fast-paced world of day trading, making it a potential best trading strategy for those with patience and a macroeconomic outlook. The core philosophy is to capture the majority of a major market trend, holding positions for weeks, months, or even years. Position traders are not concerned with minor daily price fluctuations; instead, they focus on the big picture, driven by fundamental factors and long-term technical analysis.
How It Works
A position trader's goal is to identify an asset with strong long-term potential and enter a position to capitalize on a significant, prolonged move. This requires a deep understanding of fundamental drivers like economic data, corporate earnings, and geopolitical events. Unlike short-term traders, position traders place far fewer trades, but each trade is heavily researched and carries the potential for substantial profit over time. The strategy emphasizes a "set it and forget it" mentality, but with periodic reviews to ensure the initial thesis remains valid.
For example, a position trader might buy into a commodity like copper based on a fundamental analysis predicting a global supply deficit and increased demand from green energy initiatives. They would hold this position for years, ignoring short-term volatility, until the fundamental outlook changes. This is similar to the approach taken by legendary investors like Warren Buffett, who holds stakes in companies for decades based on their underlying value and long-term growth prospects.
Actionable Tips for Implementation
To succeed with position trading, a strong analytical framework and immense patience are required.
- Conduct Thorough Fundamental Analysis: Before entering any trade, you must understand the underlying economic and business drivers. For stocks, this means analyzing financial statements; for currencies, it means studying central bank policies and economic health.
- Use Wider Stop-Losses: Because you are aiming for large moves, your stop-losses must be wide enough to accommodate normal market volatility without getting stopped out prematurely. These are often based on major technical levels on weekly or monthly charts.
- Master Position Sizing: Since you are holding trades for a long time and using wider stops, proper position sizing is critical to manage risk. Never risk more than a small percentage of your capital on a single trade.
- Stay Informed on Macro Trends: Your trading thesis is based on long-term fundamentals. Keep up with major economic reports, policy changes, and industry news that could impact your positions over the long haul.
9. Contrarian Trading Strategy
The Contrarian Trading Strategy is a psychologically demanding yet potentially highly rewarding approach, making it a unique contender for the best trading strategy. Its core principle is to deliberately go against prevailing market sentiment. A contrarian trader believes the crowd is often wrong at market extremes, driven by fear or greed. They buy when everyone else is panicking and selling, and sell when the market is euphoric and buying indiscriminately.
How It Works
A contrarian's main task is to identify points of maximum pessimism or optimism and take the opposite position. This strategy is rooted in the idea that asset prices can significantly overshoot their intrinsic value during bubbles or undershoot during panics. Profitability comes from capitalizing on the eventual mean reversion, where prices return to a more rational valuation. This requires immense conviction and the discipline to enter positions when it feels most uncomfortable.
For example, legendary investor John Templeton famously bought stocks during the Great Depression when sentiment was at its lowest. More recently, Michael Burry's "Big Short" against the U.S. housing market before the 2008 financial crisis is a prime example of a contrarian trade. He identified a bubble fueled by irrational exuberance and positioned himself to profit from its collapse while the consensus view was still overwhelmingly positive.
The video above provides further insight into the mindset required to successfully trade against the crowd.
Actionable Tips for Implementation
To implement a contrarian strategy, you need objective tools and unwavering discipline.
- Use Sentiment Indicators: Don't just guess what the crowd is thinking. Use data-driven tools like the VIX (the "fear index"), put/call ratios, and the AAII Investor Sentiment Survey to gauge market extremes.
- Wait for Confirmation: Going against the trend is risky. Wait for a sign of reversal, such as a strong bullish candlestick pattern at a market bottom, before committing significant capital. This helps avoid catching a falling knife.
- Build Positions Gradually: Since timing the exact turning point is nearly impossible, use dollar-cost averaging to build your position. Buy in smaller increments as the price moves against you to improve your average entry price.
- Maintain Iron-Clad Risk Management: Contrarian trades can move against you for longer than you expect. Use strict stop-losses and position sizing to ensure that a single wrong bet doesn't wipe out your account.
10. Grid Trading Strategy
The Grid Trading Strategy is a systematic approach that automates buying low and selling high within a predefined price range, making it a unique contender for the best trading strategy for range-bound markets. Instead of predicting a specific direction, this method thrives on volatility. Its core principle is to profit from the market's natural ebb and flow. Traders set a series of buy and sell orders at predetermined intervals above and below a central price, creating a “grid.”
How It Works
A grid trader first identifies a market that is consolidating or trading within a horizontal channel. They then place buy orders at regular intervals below the current price and sell orders at intervals above it. As the price fluctuates down, buy orders are triggered. When the price moves back up, the corresponding sell orders are executed, locking in small, consistent profits. The strategy performs best in choppy, sideways markets where prices move up and down without a strong directional bias.
For example, a forex trader might identify a stable trading range in EUR/USD between 1.0700 and 1.0800. They could set a grid with buy orders every 20 pips below 1.0750 and sell orders every 20 pips above it. As the price bounces within this range, the system automatically accumulates positions at lower levels and sells them at higher levels. This mechanical process removes emotion and aims to capitalize on price oscillations.
Actionable Tips for Implementation
To implement grid trading effectively, focus on risk management and market selection.
- Set Grid Spacing Based on Volatility: Use an indicator like Average True Range (ATR) to determine the appropriate distance between your grid levels. Wider grids are suitable for more volatile markets, while tighter grids work better in low-volatility environments.
- Manage Your Margin Carefully: A grid can open numerous positions, which can quickly consume your margin, especially if the market breaks out of your range. Always calculate the maximum potential drawdown and ensure you have enough capital to withstand it without a margin call.
- Know When to Turn It Off: This strategy is designed for ranging markets. If a strong, sustained trend emerges, the grid will accumulate losing positions. Use trend-identifying tools like moving averages or the ADX to recognize when market conditions have changed and it's time to close the grid.
- Start with a "With-the-Trend" Grid: While classic grid trading is direction-neutral, a safer variation is to only place buy orders in a confirmed uptrend or sell orders in a downtrend. This hybrid approach helps mitigate the risk of a strong move against your entire position set.
Top 10 Trading Strategies Comparison
| Strategy | Implementation Complexity 🔄 | Resource Requirements ⚡ | Expected Outcomes 📊 | Ideal Use Cases 💡 | Key Advantages ⭐ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Trend Following | Moderate – uses systematic rules and indicators | Moderate – requires data for trend indicators | Capture large, sustained price moves | Medium to long-term trending markets | Simple rules, reduces emotional trading |
| Swing Trading | Moderate – mix of technical and fundamental analysis | Low to moderate – less time-intensive than day trading | Profit from intermediate price swings | Holding positions days to weeks | Flexible time commitment, suited for part-time |
| Scalping | High – requires fast decisions and execution | High – needs advanced tech, fast data feeds | Numerous small, quick profits | Highly liquid markets, intraday | Quick profits, minimal overnight risk |
| Mean Reversion | Moderate – statistical analysis and indicators | Moderate – requires statistical tools | High win rate in sideways markets | Range-bound/sideways markets | Clear signals, good for options and systematic backtesting |
| Breakout Trading | Moderate to high – requires quick reactions | Moderate – volume and price data needed | Capture start of significant moves | Volatile markets with strong directional moves | Clear entries, good for momentum/volume confirmation |
| Momentum Trading | Moderate to high – continuous monitoring | Moderate to high – requires timely data | Profits from strong short-term trends | Trending assets with strong recent performance | Aligns with institutional flows, clear signals |
| Arbitrage Trading | Very High – requires sophisticated, fast execution | Very High – tech, capital, and connectivity | Small, consistent risk-free profits | Price inefficiencies across markets | Risk-free in theory, market efficiency contribution |
| Position Trading | Low to moderate – long-term trade setup | Low – infrequent trades and monitoring | Gains from long-term fundamental trends | Long-term market moves, fundamental analysis | Low stress, low transaction costs |
| Contrarian Trading | Moderate to high – psychological discipline needed | Moderate – sentiment data and market analysis | Profits from market reversals at extremes | Market extremes and panic/euphoria phases | Potential for superior entry/exit prices |
| Grid Trading | Moderate to high – systematic pending orders | Moderate to high – capital to maintain grids | Profits from volatility within price ranges | Sideways/ranging markets | Automated, profits in uncertain direction |
From Strategy to Success: Your Next Steps in Price Action
We have journeyed through ten distinct trading strategies, from the rapid-fire precision of Scalping to the long-term vision of Position Trading. You've seen how Trend Following capitalizes on established market direction, how Swing Trading captures medium-term price moves, and how Contrarian Trading dares to challenge the consensus. Each approach offers a unique lens through which to view market behavior, complete with its own set of rules, risk parameters, and psychological demands.
The central takeaway, however, is not to find a single "magic bullet" among these options. The search for the single best trading strategy often leads traders down a frustrating path of system-hopping and inconsistent results. True, sustainable success lies in finding the strategy that aligns perfectly with your personality, lifestyle, and risk tolerance, and then committing to its mastery.
The Unifying Principle: Mastering Price Action
Did you notice the common denominator weaving through the most effective strategies we discussed? It's not a complex indicator or an esoteric algorithm. It is price action.
Whether you are identifying a breakout, confirming a trend, or spotting a mean reversion opportunity, you are fundamentally interpreting the story told by price on the chart. This is the raw, unfiltered language of the market. Mastering price action-based techniques, such as identifying key supply and demand zones, understanding candlestick patterns, and recognizing market structure, is the foundational skill that elevates any strategy from a theoretical concept to a profitable endeavor. An over-reliance on lagging indicators can cloud your judgment, but a deep understanding of price action provides clarity and conviction.
Your Action Plan for Progress
Choosing a strategy is merely the first step. The real work, and the real reward, comes from diligent application and refinement. Here is a practical roadmap to transition from learning to earning:
- Select and Specialize: Based on the pros and cons outlined, choose one or two strategies that resonate most with your personal style. Are you patient enough for Swing Trading, or do you thrive on the high-frequency action of Scalping? Be honest with yourself.
- Backtest Rigorously: Before risking a single dollar, go back in time on your charts. Manually apply your chosen strategy's rules to historical price data. This process builds immense confidence and reveals the strategy's statistical edge (or lack thereof).
- Forward-Test in a Demo Account: Once backtesting yields positive expectancy, move to a demo account. This simulates live market conditions without financial risk, allowing you to hone your execution skills, manage your emotions, and refine your entry and exit protocols.
- Develop a Trading Plan: Your trading plan is your business plan. It must explicitly define your chosen strategy, risk management rules (e.g., max risk per trade), entry criteria, exit criteria, and the markets you will trade. Never trade without it.
- Start Small, Scale Smart: When you transition to a live account, begin with the smallest possible position size. Your initial goal is not to make a fortune, but to execute your plan flawlessly and manage your psychology under the pressure of real money. As you build consistency, you can gradually increase your size.
Ultimately, the best trading strategy is the one you can execute with unwavering discipline, day in and day out. It's not about finding a flawless system, but about flawlessly executing a system that has a positive edge. This journey requires dedication, but the potential rewards-financial freedom, location independence, and self-mastery-are well worth the effort. The path forward is not about adding more indicators; it's about deepening your understanding of the price itself.
Ready to master the art of indicator-free trading? Colibri Trader provides a comprehensive, price action-focused curriculum designed to build your skills from the ground up. Discover the proven strategies we use and learn how to read the market with clarity and confidence by visiting Colibri Trader.